Carbon nanotube biosensors
- PMID: 26579509
- PMCID: PMC4621484
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2015.00059
Carbon nanotube biosensors
Abstract
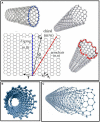
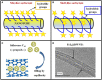
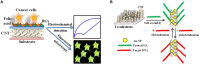
Nanomaterials possess unique features which make them particularly attractive for biosensing applications. In particular, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) can serve as scaffolds for immobilization of biomolecules at their surface, and combine several exceptional physical, chemical, electrical, and optical characteristics properties which make them one of the best suited materials for the transduction of signals associated with the recognition of analytes, metabolites, or disease biomarkers. Here we provide a comprehensive review on these carbon nanostructures, in which we describe their structural and physical properties, functionalization and cellular uptake, biocompatibility, and toxicity issues. We further review historical developments in the field of biosensors, and describe the different types of biosensors which have been developed over time, with specific focus on CNT-conjugates engineered for biosensing applications, and in particular detection of cancer biomarkers.
Keywords: biocompatibility; biosensing; cancer; carbon nanotube; fluorescence; functionalization; internalization.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Carbon Nanomaterials as Versatile Platforms for Biosensing Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Aug 28;11(9):814. doi: 10.3390/mi11090814. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in bioactive 1D and 2D carbon nanomaterials for biomedical applications.Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct;14(7):2433-2454. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.03.021. Epub 2017 May 26. Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 28552644 Review.
-
Carbon nanotube-based electrochemical biosensing platforms: fundamentals, applications, and future possibilities.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2007;1(2):181-91. doi: 10.2174/187220807780809427. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 19075840 Review.
-
Nanotubes in biosensing.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010 Sep-Oct;2(5):496-509. doi: 10.1002/wnan.94. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20803683 Review.
-
High-Performance Biosensing Systems Based on Various Nanomaterials as Signal Transducers.Biotechnol J. 2019 Jan;14(1):e1800249. doi: 10.1002/biot.201800249. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30117715 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials for Early Detection of Alzheimer's Disease.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 22;20(17):4748. doi: 10.3390/s20174748. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32842632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Trends in Fluorescent Nanomaterials-Based Bio/Chemical Sensors for Neurohormones Detection-A Review.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 15;7(38):33749-33768. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04134. eCollection 2022 Sep 27. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36188279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Soft and Dry Electrodes for Wearable Health Monitoring Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Apr 16;13(4):629. doi: 10.3390/mi13040629. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35457934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering carbon nanotubes for sensitive viral detection.Trends Analyt Chem. 2022 Aug;153:116659. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2022.116659. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Trends Analyt Chem. 2022. PMID: 35527799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gluconobacter oxydans as the Basis of a Biosensor.Biosensors (Basel). 2019 Nov 14;9(4):137. doi: 10.3390/bios9040137. Biosensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31739608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajayan P. M., Lijima S. (1993). Capillarity-induced filling of carbon nanotubes. Nature 361, 333–334. 10.1038/361333a0 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

