Efficacy of Pregabalin in Acute Postoperative Pain Under Different Surgical Categories: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26579802
- PMCID: PMC4652811
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001944
Efficacy of Pregabalin in Acute Postoperative Pain Under Different Surgical Categories: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
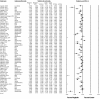
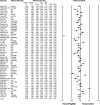
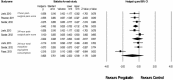
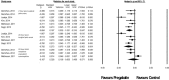
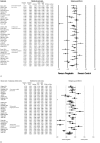
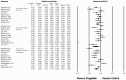
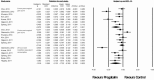
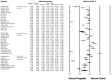
The efficacy of pregabalin in acute postsurgical pain has been demonstrated in numerous studies; however, the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of using pregabalin in various surgical procedures remain uncertain. We aim to assess the postsurgical analgesic efficacy and adverse events after pregabalin administration under different surgical categories using a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.A search of the literature was performed between August 2014 to April 2015, using PubMed, Ovid via EMBASE, Google Scholar, and ClinicalTrials.gov with no limitation on publication year or language. Studies considered for inclusion were randomized controlled trials, reporting on relevant outcomes (2-, 24-hour pain scores, or 24 hour morphine-equivalent consumption) with treatment with perioperative pregabalin.Seventy-four studies were included. Pregabalin reduced pain scores at 2 hours in all categories: cardiothoracic (Hedge's g and 95%CI, -0.442 [-0.752 to -0.132], P = 0.005), ENT (Hedge g and 95%CI, -0.684 [-1.051 to -0.316], P < 0.0001), gynecologic (Hedge g, 95%CI, -0.792 [-1.235 to -0.350], P < 0.0001), laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Hedge g, 95%CI, -0.600 [-0.989 to -0.210], P = 0.003), orthopedic (Hedge g, 95%CI, -0.507 [-0.812 to -0.202], P = 0.001), spine (Hedge g, 95%CI, -0.972 [-1.537 to -0.407], P = 0.001), and miscellaneous procedures (Hedge g, 95%CI, -1.976 [-2.654 to -1.297], P < 0.0001). Pregabalin reduced 24-hour morphine consumption in gynecologic (Hedge g, 95%CI, -1.085 [-1.582 to -0.441], P = 0.001), laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Hedge g, 95%CI, -0.886 [-1.652 to -0.120], P = 0.023), orthopedic (Hedge g, 95%CI, -0.720 [-1.118 to -0.323], P < 0.0001), spine (Hedge g, 95%CI, -1.016 [-1.732 to -0.300], P = 0.005), and miscellaneous procedures (Hedge g, 95%CI, -1.329 [-2.286 to -0.372], P = 0.006). Pregabalin resulted in significant sedation in all surgical categories except ENT, laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and gynecologic procedures. Postoperative nausea and vomiting was only significant after pregabalin in miscellaneous procedures.Analgesic effects and incidence of adverse effects of using pregabalin are not equal in different surgical categories.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Continuous intravenous perioperative lidocaine infusion for postoperative pain and recovery in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 4;6(6):CD009642. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009642.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29864216 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of preoperative administration of gabapentin/pregabalin in improving pain after total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Aug 30;17(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1231-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27577678 Free PMC article.
-
Transversus abdominis plane (TAP) blocks for prevention of postoperative pain in women undergoing laparoscopic and robotic gynaecological surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 3;4(4):CD015145. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015145.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40178137
-
Continuous intravenous perioperative lidocaine infusion for postoperative pain and recovery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 16;(7):CD009642. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009642.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 04;6:CD009642. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009642.pub3. PMID: 26184397 Updated.
Cited by
-
Effects of pregabalin on postoperative pain after hysterectomy under spinal anesthesia with intrathecal morphine: a randomized controlled trial.J Anesth. 2017 Dec;31(6):861-868. doi: 10.1007/s00540-017-2406-3. Epub 2017 Sep 16. J Anesth. 2017. PMID: 28918556 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin for treatment of post refractive surgery pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 24;44(1):409. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03300-9. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39448432
-
Effects of Gabapentinoids Premedication on Shoulder Pain and Rehabilitation Quality after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Pregabalin versus Gabapentin.Pain Res Manag. 2018 Jul 9;2018:9834059. doi: 10.1155/2018/9834059. eCollection 2018. Pain Res Manag. 2018. PMID: 30123399 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of a Single Dose Oral Pregabalin on Hemodynamic Changes and Duration of Analgesia after Spinal Anesthesia in Orthopedic Surgeries of Tibial Fractures.Iran J Pharm Res. 2018 Winter;17(Suppl):2-7. Iran J Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29796024 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Pregabalin on Postcraniotomy Pain in Patients Undergoing Supratentorial Tumor Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2019 Oct;10(4):641-645. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3399490. Epub 2019 Dec 11. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2019. PMID: 31831983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben-Menachem E. Pregabalin pharmacology and its relevance to clinical practice. Epilepsia 2004; 45 suppl 6:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Shneker BF, McAuley JW. Pregabalin: a new neuromodulator with broad therapeutic indications. Ann Pharmacother 2005; 39:2029–2037. - PubMed
-
- Hindmarch I, Trick L, Ridout F. A double-blind, placebo- and positive-internal-controlled (alprazolam) investigation of the cognitive and psychomotor profile of pregabalin in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2005; 183:133–143. - PubMed
-
- Schug SA, Zech D, Grond S. Adverse effects of systemic opioid analgesics. Drug Saf 1992; 7:200–213. - PubMed
-
- Mishriky BM, Waldron NH, Habib AS. Impact of pregabalin on acute and persistent postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth 2015; 114:10–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

