Development and Internal Validation of a Predictive Model Including Pulse Oximetry for Hospitalization of Under-Five Children in Bangladesh
- PMID: 26580403
- PMCID: PMC4651571
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143213
Development and Internal Validation of a Predictive Model Including Pulse Oximetry for Hospitalization of Under-Five Children in Bangladesh
Erratum in
-
Correction: Development and Internal Validation of a Predictive Model Including Pulse Oximetry for Hospitalization of Under-Five Children in Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 15;11(1):e0147560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147560. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26771879 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The reduction in the deaths of millions of children who die from infectious diseases requires early initiation of treatment and improved access to care available in health facilities. A major challenge is the lack of objective evidence to guide front line health workers in the community to recognize critical illness in children earlier in their course.
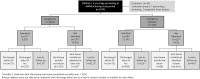
Methods: We undertook a prospective observational study of children less than 5 years of age presenting at the outpatient or emergency department of a rural tertiary care hospital between October 2012 and April 2013. Study physicians collected clinical signs and symptoms from the facility records, and with a mobile application performed recordings of oxygen saturation, heart rate and respiratory rate. Facility physicians decided the need for hospital admission without knowledge of the oxygen saturation. Multiple logistic predictive models were tested.
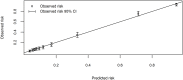
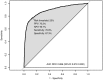
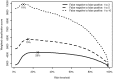
Findings: Twenty-five percent of the 3374 assessed children, with a median (interquartile range) age of 1.02 (0.42-2.24), were admitted to hospital. We were unable to contact 20% of subjects after their visit. A logistic regression model using continuous oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, temperature and age combined with dichotomous signs of chest indrawing, lethargy, irritability and symptoms of cough, diarrhea and fast or difficult breathing predicted admission to hospital with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.89 (95% confidence interval -CI: 0.87 to 0.90). At a risk threshold of 25% for admission, the sensitivity was 77% (95% CI: 74% to 80%), specificity was 87% (95% CI: 86% to 88%), positive predictive value was 70% (95% CI: 67% to 73%) and negative predictive value was 91% (95% CI: 90% to 92%).
Conclusion: A model using oxygen saturation, respiratory rate and temperature in combination with readily obtained clinical signs and symptoms predicted the need for hospitalization of critically ill children. External validation of this model in a community setting will be required before adoption into clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF. Committing to Child Survival: A Promise Renewed. 2012. UNICEF Progress Report 2012. Available: http://www.un.org/ru/publications/pdfs/renewed_%20progress%20report%2020...
-
- Launay E, Gras-Le Guen C, Martinot A, Assathiany R, Martin E, Blanchais T, et al. Why children with severe bacterial infection die: A population–based study of determinants and consequences of suboptimal care with a special emphasis on methodological issues. PLoS One. 2014; 9 (9): e107286 10.1371/journal.pone.0107286 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nair H, Simões EA, Rudan I, Gessner BD, Azziz-Baumgartner E, Zhang JSF, et al. Global and regional burden of hospital admissions for severe acute lower respiratory infections in young children in 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2013; 6736(12): 4–6. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61901-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

