Functional Characterization of IPSC-Derived Brain Cells as a Model for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 26581106
- PMCID: PMC4651558
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143238
Functional Characterization of IPSC-Derived Brain Cells as a Model for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
X-ALD is an inherited neurodegenerative disorder where mutations in the ABCD1 gene result in clinically diverse phenotypes: the fatal disorder of cerebral childhood ALD (cALD) or a milder disorder of adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN). The various models used to study the pathobiology of X-ALD disease lack the appropriate presentation for different phenotypes of cALD vs AMN. This study demonstrates that induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSC) derived brain cells astrocytes (Ast), neurons and oligodendrocytes (OLs) express morphological and functional activities of the respective brain cell types. The excessive accumulation of saturated VLCFA, a "hallmark" of X-ALD, was observed in both AMN OLs and cALD OLs with higher levels observed in cALD OLs than AMN OLs. The levels of ELOVL1 (ELOVL Fatty Acid Elongase 1) mRNA parallel the VLCFA load in AMN and cALD OLs. Furthermore, cALD Ast expressed higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines than AMN Ast and control Ast with or without stimulation with lipopolysaccharide. These results document that IPSC-derived Ast and OLs from cALD and AMN fibroblasts mimic the respective biochemical disease phenotypes and thus provide an ideal platform to investigate the mechanism of VLCFA load in cALD OLs and VLCFA-induced inflammatory disease mechanisms of cALD Ast and thus for testing of new therapeutics for AMN and cALD disease of X-ALD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


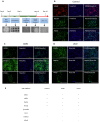
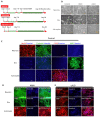



Similar articles
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell models from X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy patients.Ann Neurol. 2011 Sep;70(3):402-9. doi: 10.1002/ana.22486. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Ann Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21721033
-
Generation and Characterization of Human iPSC-Derived Astrocytes with Potential for Modeling X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Phenotypes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 13;26(4):1576. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041576. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004040 Free PMC article.
-
IPSC-Derived Astrocytes to Model Neuroinflammatory and Metabolic Responses in X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy.J Biotechnol Biomed. 2023;6(3):281-293. doi: 10.26502/jbb.2642-91280091. Epub 2023 Aug 4. J Biotechnol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 38077449 Free PMC article.
-
Pathomechanisms underlying X-adrenoleukodystrophy: a three-hit hypothesis.Brain Pathol. 2010 Jul;20(4):838-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00392.x. Brain Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20626745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy].Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2007 Dec;68(6):403-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2007.04.002. Epub 2007 May 29. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2007. PMID: 17532287 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Dendrimer-N-acetyl-L-cysteine modulates monophagocytic response in adrenoleukodystrophy.Ann Neurol. 2018 Sep;84(3):452-462. doi: 10.1002/ana.25303. Ann Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30069915 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of an immortalized astrocytic cell line from Abcd1-deficient H-2KbtsA58 mice to facilitate the study of the role of astrocytes in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Heliyon. 2021 Feb 11;7(2):e06228. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06228. eCollection 2021 Feb. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33659749 Free PMC article.
-
GSNO promotes functional recovery in experimental TBI by stabilizing HIF-1α.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Mar 15;340:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.10.037. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 27780722 Free PMC article.
-
The pathology of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: tissue specific changes as a clue to pathophysiology.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Mar 28;19(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03105-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38549180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etiology and treatment of adrenoleukodystrophy: new insights from Drosophila.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Jun 15;11(6):dmm031286. doi: 10.1242/dmm.031286. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29739804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moser H. Smith KD, Watkins PA, Powers J, Moser AB (2001) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, in The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill, New York: Scriver C., ed.
-
- Mosser J, Douar AM, Sarde CO, Kioschis P, Feil R, et al. (1993) Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature 361: 726–730. - PubMed
-
- Dubois-Dalcq M, Feigenbaum V, Aubourg P (1999) The neurobiology of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, a demyelinating peroxisomal disorder. Trends Neurosci 22: 4–12. - PubMed
-
- Berger J, Gartner J (2006) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: clinical, biochemical and pathogenetic aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763: 1721–1732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C06 RR-018823/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR-015455/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS72511/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS022576/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS064195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS022576/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-22576/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-64195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR018823/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR015455/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072511/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-37766/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS037766/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

