Metabolic Control With the Bio-inspired Artificial Pancreas in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A 24-Hour Randomized Controlled Crossover Study
- PMID: 26581881
- PMCID: PMC4773972
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296815616134
Metabolic Control With the Bio-inspired Artificial Pancreas in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A 24-Hour Randomized Controlled Crossover Study
Abstract
Background: The Bio-inspired Artificial Pancreas (BiAP) is a closed-loop insulin delivery system based on a mathematical model of beta-cell physiology and implemented in a microchip within a low-powered handheld device. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the BiAP over 24 hours, followed by a substudy assessing the safety of the algorithm without and with partial meal announcement. Changes in lactate and 3-hydroxybutyrate concentrations were investigated for the first time during closed-loop.
Methods: This is a prospective randomized controlled open-label crossover study. Participants were randomly assigned to attend either a 24-hour closed-loop visit connected to the BiAP system or a 24-hour open-loop visit (standard insulin pump therapy). The primary outcome was percentage time spent in target range (3.9-10 mmol/l) measured by sensor glucose. Secondary outcomes included percentage time in hypoglycemia (<3.9 mmol/l) and hyperglycemia (>10 mmol/l). Participants were invited to attend for an additional visit to assess the BiAP without and with partial meal announcements.
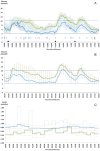
Results: A total of 12 adults with type 1 diabetes completed the study (58% female, mean [SD] age 45 [10] years, BMI 25 [4] kg/m(2), duration of diabetes 22 [12] years and HbA1c 7.4 [0.7]% [58 (8) mmol/mol]). The median (IQR) percentage time in target did not differ between closed-loop and open-loop (71% vs 66.9%, P = .9). Closed-loop reduced time spent in hypoglycemia from 17.9% to 3.0% (P < .01), but increased time was spent in hyperglycemia (10% vs 28.9%, P = .01). The percentage time in target was higher when all meals were announced during closed-loop compared to no or partial meal announcement (65.7% [53.6-80.5] vs 45.5% [38.2-68.3], P = .12).
Conclusions: The BiAP is safe and achieved equivalent time in target as measured by sensor glucose, with improvement in hypoglycemia, when compared to standard pump therapy.
Keywords: Bio-inspired Artificial Pancreas; closed-loop insulin delivery; diabetes technology; type 1 diabetes.
© 2015 Diabetes Technology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. July 2008. NICE technology appraisal guidance 151. Available at: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta151.
-
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group, Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1464-1476. - PubMed
-
- Bergenstal RM, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, et al. Effectiveness of sensor-augmented insulin-pump therapy in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2010;22;363:311-320. - PubMed
-
- Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, et al. Threshold-based insulin-pump interruption for reduction of hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:224-232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

