Loss of Either Rac1 or Rac3 GTPase Differentially Affects the Behavior of Mutant Mice and the Development of Functional GABAergic Networks
- PMID: 26582364
- PMCID: PMC4712809
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhv274
Loss of Either Rac1 or Rac3 GTPase Differentially Affects the Behavior of Mutant Mice and the Development of Functional GABAergic Networks
Abstract
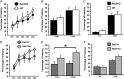
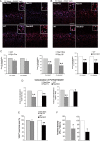
Rac GTPases regulate the development of cortical/hippocampal GABAergic interneurons by affecting the early development and migration of GABAergic precursors. We have addressed the function of Rac1 and Rac3 proteins during the late maturation of hippocampal interneurons. We observed specific phenotypic differences between conditional Rac1 and full Rac3 knockout mice. Rac1 deletion caused greater generalized hyperactivity and cognitive impairment compared with Rac3 deletion. This phenotype matched with a more evident functional impairment of the inhibitory circuits in Rac1 mutants, showing higher excitability and reduced spontaneous inhibitory currents in the CA hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Morphological analysis confirmed a differential modification of the inhibitory circuits: deletion of either Rac caused a similar reduction of parvalbumin-positive inhibitory terminals in the pyramidal layer. Intriguingly, cannabinoid receptor-1-positive terminals were strongly increased only in the CA1 of Rac1-depleted mice. This increase may underlie the stronger electrophysiological defects in this mutant. Accordingly, incubation with an antagonist for cannabinoid receptors partially rescued the reduction of spontaneous inhibitory currents in the pyramidal cells of Rac1 mutants. Our results show that Rac1 and Rac3 have independent roles in the formation of GABAergic circuits, as highlighted by the differential effects of their deletion on the late maturation of specific populations of interneurons.
Keywords: CB1R; VGAT; hyperactivity; inhibitory synapses; neuronal maturation.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Disruption of ArhGAP15 results in hyperactive Rac1, affects the architecture and function of hippocampal inhibitory neurons and causes cognitive deficits.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 7;6:34877. doi: 10.1038/srep34877. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27713499 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 and rac3 GTPases control synergistically the development of cortical and hippocampal GABAergic interneurons.Cereb Cortex. 2014 May;24(5):1247-58. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs402. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Cereb Cortex. 2014. PMID: 23258346 Free PMC article.
-
An Optogenetic Approach for Investigation of Excitatory and Inhibitory Network GABA Actions in Mice Expressing Channelrhodopsin-2 in GABAergic Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 1;36(22):5961-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3482-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27251618 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases differently influence the morphological maturation of dendritic spines in hippocampal neurons.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 1;14(8):e0220496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220496. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31369617 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases during the development of cortical and hippocampal GABAergic interneurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Sep 25;8:307. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00307. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25309333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Rac3 GTPase in Neuronal Development, Neurodevelopmental Disorders, and Cancer.Cells. 2019 Sep 11;8(9):1063. doi: 10.3390/cells8091063. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31514269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The p.R66W Variant in RAC3 Causes Severe Fetopathy Through Variant-Specific Mechanisms.Cells. 2024 Dec 9;13(23):2032. doi: 10.3390/cells13232032. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682779 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of ArhGAP15 results in hyperactive Rac1, affects the architecture and function of hippocampal inhibitory neurons and causes cognitive deficits.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 7;6:34877. doi: 10.1038/srep34877. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27713499 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-Family Small GTPases: From Highly Polarized Sensory Neurons to Cancer Cells.Cells. 2019 Jan 28;8(2):92. doi: 10.3390/cells8020092. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30696065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Method to Culture GABAergic Interneurons Derived from the Medial Ganglionic Eminence.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Jan 8;11:423. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00423. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29358905 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolis A, Corbetta S, Cioce A, de Curtis I. 2003. Differential distribution of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases in the developing mouse brain: implications for a role of Rac3 in Purkinje cell differentiation. Eur J Neurosci. 18:2417–2424. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G. 2002. Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron. 33:325–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

