Arl13b and the exocyst interact synergistically in ciliogenesis
- PMID: 26582389
- PMCID: PMC4713133
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E15-02-0061
Arl13b and the exocyst interact synergistically in ciliogenesis
Abstract
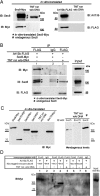
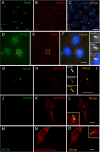
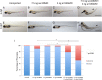
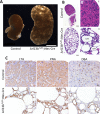
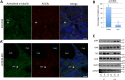
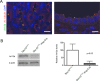
Arl13b belongs to the ADP-ribosylation factor family within the Ras superfamily of regulatory GTPases. Mutations in Arl13b cause Joubert syndrome, which is characterized by congenital cerebellar ataxia, hypotonia, oculomotor apraxia, and mental retardation. Arl13b is highly enriched in cilia and is required for ciliogenesis in multiple organs. Nevertheless, the precise role of Arl13b remains elusive. Here we report that the exocyst subunits Sec8, Exo70, and Sec5 bind preferentially to the GTP-bound form of Arl13b, consistent with the exocyst being an effector of Arl13b. Moreover, we show that Arl13b binds directly to Sec8 and Sec5. In zebrafish, depletion of arl13b or the exocyst subunit sec10 causes phenotypes characteristic of defective cilia, such as curly tail up, edema, and abnormal pronephric kidney development. We explored this further and found a synergistic genetic interaction between arl13b and sec10 morphants in cilia-dependent phenotypes. Through conditional deletion of Arl13b or Sec10 in mice, we found kidney cysts and decreased ciliogenesis in cells surrounding the cysts. Moreover, we observed a decrease in Arl13b expression in the kidneys from Sec10 conditional knockout mice. Taken together, our results indicate that Arl13b and the exocyst function together in the same pathway leading to functional cilia.
© 2016 Seixas et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures


References
-
- Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N. The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2006;7:125–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- R21 DK070980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5G12MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R03DK100738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20GM103456-06A1-8293/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069909/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK074038/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM090158/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK087852/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK100738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM090158/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM110663/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS056380/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30DK074038/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008490/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103457/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH087977/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DK069909/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK070980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32MH087977/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1K01DK087852/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM008490/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000820/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

