ANTIOXIDANT CAPACITY OF WYOMING BIG SAGEBRUSH (ARTEMISIA TRIDENTATA SSP. WYOMINGENSIS) VARIES SPATIALLY AND IS NOT RELATED TO THE PRESENCE OF A SAGEBRUSH DIETARY SPECIALIST
- PMID: 26582971
- PMCID: PMC4646226
- DOI: 10.3398/064.075.0109
ANTIOXIDANT CAPACITY OF WYOMING BIG SAGEBRUSH (ARTEMISIA TRIDENTATA SSP. WYOMINGENSIS) VARIES SPATIALLY AND IS NOT RELATED TO THE PRESENCE OF A SAGEBRUSH DIETARY SPECIALIST
Abstract
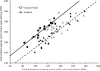
Sagebrush (Artemisia spp.) in North America is an abundant native plant species that is ecologically and evolutionarily adapted to have a diverse array of biologically active chemicals. Several of these chemicals, specifically polyphenols, have antioxidant activity that may act as biomarkers of biotic or abiotic stress. This study investigated the spatial variation of antioxidant capacity, as well as the relationship between a mammalian herbivore and antioxidant capacity in Wyoming big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata wyomingensis). We quantified and compared total polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of leaf extracts from sagebrush plants from different spatial scales and at different levels of browsing by a specialist mammalian herbivore, the pygmy rabbit (Brachylagus idahoensis). We found that antioxidant capacity of sagebrush extracts was positively correlated with total polyphenol content. Antioxidant capacity varied spatially within and among plants. Antioxidant capacity in sagebrush was not related to either browsing intensity or duration of association with rabbits. We propose that the patterns of antioxidant capacity observed in sagebrush may be a result of spatial variation in abiotic stress experienced by sagebrush. Antioxidants could therefore provide a biomarker of environmental stress for sagebrush that could aid in management and conservation of this plant in the threatened sagebrush steppe.
Figures
References
-
- Ainsworth EA, Gillespie KM. Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Nature Protocols. 2007;2:875–877. - PubMed
-
- Anjum SA, Xie XY, Wang LC, F Saleem M, Man C, Lei W. Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress. African Journal of Agricultural Research. 2011;6:2026–2032.
-
- Anter J, Romero-Jimenez M, Fernandez-Bedmar Z, Villatoro-Pulido M, Analla M, Alonso-Moraga A, Munoz-Serrano A. Antigenotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis induction by apigenin, bisabolol, and protocatechuic acid. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2011;14:276–283. - PubMed
-
- Arantes FFP, Barbosa LCA, Maltha CRA, Demuner AJ, Fidencio PH, Carneiro JWM. A quantum chemical and chemometric study of sesquiterpene lactones with cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Journal of Chemometrics. 2011;25:401–407.
-
- Bahnweg G, Schubert R, Kehr RD, Muller-Starck G, Heller W, Langebartels C, San-dermann H. Controlled inoculation of Norway spruce (Picea abies) with Sirococcus conigenus: PCR-based quantification of the pathogen in host tissue and infection-related increase of phenolic metabolites. Trees. 2000;14:435–441.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
