Palladium-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Aryl Nitromethanes
- PMID: 26584680
- PMCID: PMC4672744
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02793
Palladium-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Aryl Nitromethanes
Abstract
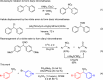
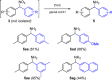
Catalytic conditions for the α-arylation of aryl nitromethanes have been discovered using parallel microscale experimentation, despite two prior reports of the lack of reactivity of these aryl nitromethane precursors. The method efficiently provides a variety of substituted, isolable diaryl nitromethanes. In addition, it is possible to sequentially append two different aryl groups to nitromethane. Mild oxidation conditions were identified to afford the corresponding benzophenones via the Nef reaction, and reduction conditions were optimized to afford several diaryl methylamines.
Figures




References
-
- Ballini R.; Bosica G.; Fiorini D.; Palmieri A.; Petrini M. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 933–97110.1021/cr040602r. - DOI - PubMed
- Ono N.The Nitro Group in Organic Synthesis; Wiley-VCH: New York, 2001.
- Rosini G.; Ballini R. Synthesis 1988, 1988, 833–84710.1055/s-1988-27726. - DOI
- Feuer H., Nielsen A. T., Eds. Nitro Compounds: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Chemistry; VCH Publishers: New York, 1990.
-
- Ballini R.; Palmieri A.; Righi P. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 12099–1212110.1016/j.tet.2007.09.024. - DOI
- Wade P. A.; Morrow S. D.; Hardinger S. A. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 365–36710.1021/jo00341a040. - DOI
- Luzzio F. A. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 915–94510.1016/S0040-4020(00)00965-0. - DOI
- Aleksandrowicz P.; Piotrowska H.; Sas W. Tetrahedron 1982, 38, 1321–132710.1016/0040-4020(82)85120-X. - DOI
- Gildner P. G.; Gietter A. A. S.; Cui D.; Watson D. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9942–994510.1021/ja304561c. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Henry L. C. R. Acad. Sci. Ser. C 1895, 120, 1265–1268.
- Henry L. Bull. Soc. Chim. France 1895, 13, 999.
- Adams H.; Anderson J. C.; Peace S.; Pennell A. M. K. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 9932–993410.1021/jo981700d. - DOI
-
- Feuer H.; Friedman H. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 187–19010.1021/jo00890a008. - DOI
-
- Zarchi M. A. K.; Zarei A. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2005, 52, 309–31110.1002/jccs.200500047. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

