Prevention of bacterial infections in the newborn by pre-delivery administration of azithromycin: Study protocol of a randomized efficacy trial
- PMID: 26585192
- PMCID: PMC4653934
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-015-0737-3
Prevention of bacterial infections in the newborn by pre-delivery administration of azithromycin: Study protocol of a randomized efficacy trial
Abstract
Background: Neonatal deaths, estimated at approximately 4 million annually, now account for almost 40% of global mortality in children aged under-five. Bacterial sepsis is a leading cause of neonatal mortality. Assuming the mother is the main source for bacterial transmission to newborns, the primary objective of the trial is to determine the impact of one oral dose of azithromycin, given to women in labour, on the newborn's bacterial carriage in the nasopharynx. Secondary objectives include the impact of the intervention on bacterial colonization in the baby and the mother during the first month of life.
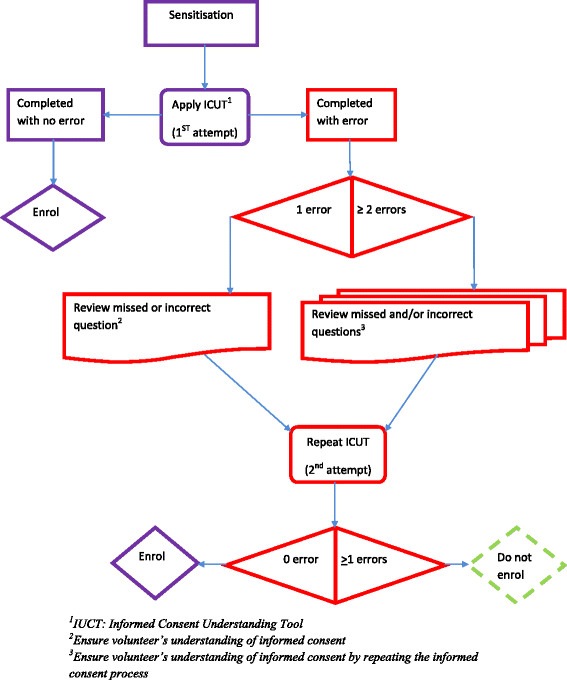
Methods/design: This is a Phase III, double -blind, placebo controlled randomized clinical trial in which 830 women in labour were randomized to either a single dose of 2 g oral azithromycin or placebo (ratio 1:1). The trial included pregnant women in labour aged 18 to 45 years attending study health centres in the Western Gambia. A post-natal check of the mother and baby was conducted at the health centre by study clinicians before discharge and 8-10 days after delivery. Home follow up visits were conducted daily during the first week and then weekly until week 8 after delivery. Vaginal swabs and breast milk samples were collected from the mothers, and the pathogens Streptococcus pneumoniae, Group B Streptococcus (GBS) and Staphylococcus aureus were isolated from the study samples. For bacterial isolates, susceptibility pattern to azithromycin was determined using disk diffusion and E-test. Eye swabs were collected from newborns with eye discharge during the follow up period, and Chlamydial infection was assessed using molecular methods.
Discussion: This is a proof-of-concept study to assess the impact of antibiotic preventive treatment of women during labour on bacterial infections in the newborn. If the trial confirms this hypothesis, the next step will be to assess the impact of this intervention on neonatal sepsis. The proposed intervention should be easily implementable in developing countries.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier--NCT01800942--First received: February 26, 2013.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- MR/J010391/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A900_1119/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/K011944/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/J010391/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K012126/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical