Three-dimensional spectral domain optical coherence tomography and light microscopy of an intravitreal parasite
- PMID: 26585462
- PMCID: PMC4653122
- DOI: 10.1186/s12348-015-0064-x
Three-dimensional spectral domain optical coherence tomography and light microscopy of an intravitreal parasite
Abstract
Background: Various imaging modalities play a role in diagnosing parasitic infections of the eye. We describe the spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) findings of an intravitreal parasite with subsequent evaluation by light microscopy.
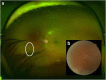
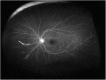
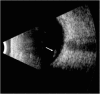
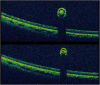
Findings: This is a case report of a 37-year-old Ecuadorian man who presented with uveitic glaucoma and a new floater in his left eye for 1 week's duration. Full ophthalmic examination revealed an intravitreal parasite. Color fundus photography, fluorescein angiography (FA), ocular ultrasonography (US), and SD-OCT were performed. The parasite was removed via 23-gauge pars plana vitrectomy and sent to pathology for evaluation. Color fundus photography and ocular ultrasonography demonstrated an elongated foreign body within the vitreous above the retina. FA demonstrated minimal vascular changes in the vicinity of the parasite. SD-OCT was utilized to visualize the parasite and to create a three-dimensional (3D) image. The parasite was determined to be most consistent with Gnathostoma spp. by morphologic analysis.
Conclusions: This is the first reported case of SD-OCT of an intravitreal parasite with corresponding evaluation by pathology. SD-OCT allows non-invasive, high-resolution visualization and 3D reconstruction of parasitic anatomy which may help establish tomographic criteria for species identification.
Keywords: Gnathostoma; Gnathostomiasis; Ophthalmomyiasis; Optical coherence tomography; Parasitic infection; Retinal imaging.
Figures


Similar articles
-
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY ANGIOGRAPHY IMAGING OF CHOROIDAL NEOVASCULARIZATION SECONDARY TO CHOROIDAL RUPTURE TREATED BY INTRAVITREAL RANIBIZUMAB.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2022 Mar 1;16(2):222-225. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000932. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2022. PMID: 31652192
-
In Vivo 3D Imaging of Retinal Neovascularization Using Multimodal Photoacoustic Microscopy and Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging.J Imaging. 2018 Dec;4(12):150. doi: 10.3390/jimaging4120150. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Imaging. 2018. PMID: 31681820 Free PMC article.
-
SD OCT features of dry arcuate longstanding retinal folds.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2011 Mar-Apr;21(2):215-7. doi: 10.5301/ejo.2010.509. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 20872358
-
Clinical applications of spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal diseases.Biomed J. 2016 Apr;39(2):107-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Biomed J. 2016. PMID: 27372166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in equine ophthalmic imaging enhance understanding of ocular and orbital anatomy and disease in standing sedated horses.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024 Oct 25;262(S2):S47-S56. doi: 10.2460/javma.24.06.0376. Print 2024 Dec 1. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39454619 Review.
Cited by
-
A case of ophthalmomyiasis interna in the Pacific Northwest.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2017 Feb 3;6:11-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2017.01.002. eCollection 2017 Jun. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29260045 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Gnathostomiasis-Update of Earlier Survey.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017 Oct;97(4):1232-1234. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0133. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017. PMID: 28722600 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

