Diagnostic accuracy and clinical relevance of an inflammatory biomarker panel for sepsis in adult critically ill patients
- PMID: 26586579
- PMCID: PMC4716883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.10.003
Diagnostic accuracy and clinical relevance of an inflammatory biomarker panel for sepsis in adult critically ill patients
Abstract
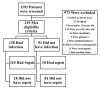
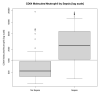
The objective of this study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), and cellular immune markers levels in sepsis. This was a prospective observational study in adult intensive care unit (ICU) patients, between 2012 and 2014. The 8-color flow cytometric biomarker panel included CD64, CD163, and HLA-DR. Index test results were compared with sepsis, using receiver operating characteristic curve analyses. Multivariate logistic regression assessed the relationship of sets of markers with the probability of sepsis. Of 219 enrolled patients, 120 had sepsis. C-statistic was the highest for CRP (0.86) followed by neutrophil CD64 expression (0.83), procalcitonin (0.82), and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) IV (0.72). After adjustment for APACHE IV, the combination of CRP, PCT, and neutrophil CD64 measure remained a significant predictor of sepsis with an excellent AUC (0.90). In a targeted ICU population at increased risk of sepsis, CRP, PCT, and neutrophil CD64 combined improve the diagnostic accuracy of sepsis.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; CD64; Procalcitonin; Sensitivity and specificity; Sepsis; Study of diagnostic accuracy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Rello J, Marshall J, et al. EPIC II Group of Investigators International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA. 2009;302:2323–2329. - PubMed
-
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, Pilcher D, Bellomo R. Mortality Related to Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Among Critically Ill Patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000-2012. JAMA. 2014;311:1308–1316. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, O'Brien J, Machado FR, Jimenez E, GSA Executive Board and WSD Executive Board The burden of sepsis-a call to action in support of World Sepsis Day 2013. J Crit Care. 2013;28:526–528. - PubMed
-
- Simon L, Gauvin F, Amre DK, Saint-Louis P, Lacroix J. Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as markers of bacterial infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:206–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

