The effects of precipitation, river discharge, land use and coastal circulation on water quality in coastal Maine
- PMID: 26587258
- PMCID: PMC4632571
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.140429
The effects of precipitation, river discharge, land use and coastal circulation on water quality in coastal Maine
Abstract
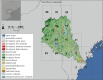
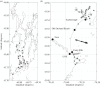
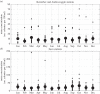
Faecal pollution in stormwater, wastewater and direct run-off can carry zoonotic pathogens to streams, rivers and the ocean, reduce water quality, and affect both recreational and commercial fishing areas of the coastal ocean. Typically, the closure of beaches and commercial fishing areas is governed by the testing for the presence of faecal bacteria, which requires an 18-24 h period for sample incubation. As water quality can change during this testing period, the need for accurate and timely predictions of coastal water quality has become acute. In this study, we: (i) examine the relationship between water quality, precipitation and river discharge at several locations within the Gulf of Maine, and (ii) use multiple linear regression models based on readily obtainable hydrometeorological measurements to predict water quality events at five coastal locations. Analysis of a 12 year dataset revealed that high river discharge and/or precipitation events can lead to reduced water quality; however, the use of only these two parameters to predict water quality can result in a number of errors. Analysis of a higher frequency, 2 year study using multiple linear regression models revealed that precipitation, salinity, river discharge, winds, seasonality and coastal circulation correlate with variations in water quality. Although there has been extensive development of regression models for freshwater, this is one of the first attempts to create a mechanistic model to predict water quality in coastal marine waters. Model performance is similar to that of efforts in other regions, which have incorporated models into water resource managers' decisions, indicating that the use of a mechanistic model in coastal Maine is feasible.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; coastal water quality; multiple linear regression models.
Figures






References
-
- Olyphant GA, Thomas J, Whitman RL, Harper D. 2003. Characterization and statistical modeling of bacterial (Escherichia coli) outflows from watersheds that discharge into southern Lake Michigan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 81, 289–300. (doi:10.1023/A:1021345512203) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fayer R, Dubey JP, Lindsay DS. 2004. Zoonotic protozoa: from land to sea. Trends Parasitol. 20, 531–536. (doi:10.1016/j.pt.2004.08.008) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nevers MB, Whitman RL. 2005. Nowcast modeling of Escherichia coli concentrations at multiple urban beaches of southern Lake Michigan. Water Res. 39, 5250–5260. (doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.012) - DOI - PubMed
-
- He L-M, He Z-L. 2008. Water quality prediction of marine recreational beaches receiving watershed baseflow and stormwater runoff in southern California, USA. Water Res. 42, 2563–3573. (doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.01.002) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thupaki P, Phanikumar MS, Beletsky D, Schwab DJ, Nevers MB, Whitman RL. 2010. Budget analysis of Escherichia coli at a southern Lake Michigan beach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1010–1016. (doi:10.1021/es902232a) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

