Clinical and radiographical evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine and propolis as pulpotomy medicaments in primary teeth
- PMID: 26587413
- PMCID: PMC4650523
- DOI: 10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.276
Clinical and radiographical evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine and propolis as pulpotomy medicaments in primary teeth
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine and Propolis as pulpotomy medicaments in primary dentition, both clinically and radiographically.
Materials and methods: A total of 75 healthy 3 to 10 yr old children each having at least one carious primary molar tooth were selected. Random assignment of the pulpotomy medicaments was done as follows: Group I, MTA; Group II, Biodentine; Group III, Propolis. All the pulpotomized teeth were evaluated at 3, 6, and 9 mon clinically and radiographically, based on the scoring criteria system.
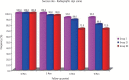
Results: The clinical success rates were found to be similar among the three groups at 3 and 6 mon where as a significant decrease in success rate was observed in Group III (84%) compared to both Group I (100%) and Group II (100%) at 9 mon. Radiographic success rates over a period of 9 mon in Groups I, II, and III were 92, 80, and 72%, respectively.
Conclusions: Teeth treated with MTA and Biodentine showed more favorable clinical and radiographic success as compared to Propolis at 9 mon follow-up.
Keywords: Biodentine; Mineral trioxide aggregate; Pulpotomy; Vital pulp therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Caicedo R, Abbott PV, Alongi DJ, Alarcon MY. Clinical, radiographic and histological analysis of the effects of mineral trioxide aggregate used in direct pulp capping and pulpotomies of primary teeth. Aust Dent J. 2006;51:297–305. - PubMed
-
- Magnusson B. Attempts to predict prognosis of pulpotomy in primary molars. Scand J Dent Res. 1970;78:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Ranly DM. Pulpotomy therapy in primary teeth: new modalities for old rationales. Pediatr Dent. 1994;16:403–409. - PubMed
-
- Eidelman E, Holan G, Fuks AB. Mineral trioxide aggregate vs. formocresol in pulpotomized primary molars: a preliminary report. Pediatr Dent. 2001;23:15–18. - PubMed
-
- Myers DR, Shoaf HK, Dirksen TR, Pashley DH, Whitford GM, Reynolds KE. Distribution of 14C-formaldehyde after pulpotomy with formocresol. J Am Dent Assoc. 1978;96:805–813. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

