Effect of dentin treatment on proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells
- PMID: 26587415
- PMCID: PMC4650525
- DOI: 10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.290
Effect of dentin treatment on proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells
Abstract
Objectives: Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) is an excellent bactericidal agent, but it is detrimental to stem cell survival, whereas intracanal medicaments such as calcium hydroxide (Ca[OH]2) promote the survival and proliferation of stem cells. This study evaluated the effect of sequential NaOCl and Ca[OH]2 application on the attachment and differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs).
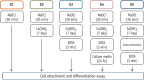
Materials and methods: DPSCs were obtained from human third molars. All dentin specimens were treated with 5.25% NaOCl for 30 min. DPSCs were seeded on the dentin specimens and processed with additional 1 mg/mL Ca[OH]2, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment, file instrumentation, or a combination of these methods. After 7 day of culture, we examined DPSC morphology using scanning electron microscopy and determined the cell survival rate with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. We measured cell adhesion gene expression levels after 4 day of culture and odontogenic differentiation gene expression levels after 4 wk using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
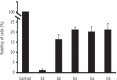
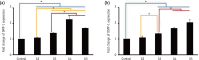
Results: DPSCs did not attach to the dentin in the NaOCl-treated group. The gene expression levels of fibronectin-1 and secreted phosphoprotein-1 gene in both the Ca[OH]2- and the EDTA-treated groups were significantly higher than those in the other groups. All Ca[OH]2-treated groups showed higher expression levels of dentin matrix protein-1 than that of the control. The dentin sialophosphoprotein level was significantly higher in the groups treated with both Ca[OH]2 and EDTA.
Conclusions: The application of Ca[OH]2 and additional treatment such as EDTA or instrumentation promoted the attachment and differentiation of DPSCs after NaOCl treatment.
Keywords: Calcium hydroxide; Cell attachment; Cell differentiation; Dental pulp stem cells; Regenerative endodontics; Sodium hypochlorite.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of EDTA on attachment and differentiation of dental pulp stem cells.J Endod. 2014 Jun;40(6):811-7. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Oct 13. J Endod. 2014. PMID: 24862708
-
Attachment and proliferation of dental pulp stem cells on dentine treated with different regenerative endodontic protocols.Int Endod J. 2017 Jul;50(7):667-675. doi: 10.1111/iej.12669. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Int Endod J. 2017. PMID: 27272393
-
Effect of benzalkonium chloride addition to EDTA on attachment and proliferation of dental pulp stem cells on dentin and on transforming growth factor-β1 release.Odontology. 2021 Apr;109(2):313-320. doi: 10.1007/s10266-020-00545-5. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Odontology. 2021. PMID: 32770280
-
Effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on proliferation, osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation, and mechanosensitive gene expression of human dental pulp stem cells.Tissue Cell. 2022 Dec;79:101955. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101955. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Tissue Cell. 2022. PMID: 36265367
-
Potential of irrigants and medicaments in regenerative endodontics: insights from a systematic review on dentin growth factor release.Odontology. 2025 Jun 15. doi: 10.1007/s10266-025-01128-y. Online ahead of print. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 40517172 Review.
Cited by
-
Odontoblast-like differentiation and mineral formation of pulpsphere derived cells on human root canal dentin in vitro.Head Face Med. 2017 Dec 8;13(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13005-017-0156-y. Head Face Med. 2017. PMID: 29221472 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of erbium yttrium aluminium garnet laser dentin conditioning on dental pulp stem cells viability.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 29;10(5):e26954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26954. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38449629 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Influence of Various Concentrations of Sodium Hypochlorite on Stem Cell Derived From Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth (SHED) Proliferation and Differentiation.Cureus. 2022 Dec 27;14(12):e33024. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33024. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36726895 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Extracellular Matrix Glycoproteins Fibronectin and Laminin-5 on Dental Pulp Stem Cell Phenotypes and Responsiveness.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Feb 8;14(2):91. doi: 10.3390/jfb14020091. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36826890 Free PMC article.
-
Odontoblast-like Cytodifferentiation of Dental Stem Cells: A Review.Iran Endod J. 2020 Spring;15(2):79-89. doi: 10.22037/iej.v15i2.27569. Iran Endod J. 2020. PMID: 36704441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jung IY, Lee SJ, Hargreaves KM. Biologically based treatment of immature permanent teeth with pulpal necrosis: a case series. J Endod. 2008;34:876–887. - PubMed
-
- Bose R, Nummikoski P, Hargreaves K. A retrospective evaluation of radiographic outcomes in immature teeth with necrotic root canal systems treated with regenerative endodontic procedures. J Endod. 2009;35:1343–1349. - PubMed
-
- Ding RY, Cheung GS, Chen J, Yin XZ, Wang QQ, Zhang CF. Pulp revascularization of immature teeth with apical periodontitis: a clinical study. J Endod. 2009;35:745–749. - PubMed
-
- Banchs F, Trope M. Revascularization of immature permanent teeth with apical periodontitis: new treatment protocol? J Endod. 2004;30:196–200. - PubMed
-
- Thibodeau B, Trope M. Pulp revascularization of a necrotic infected immature permanent tooth: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dent. 2007;29:47–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

