The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
- PMID: 26587416
- PMCID: PMC4650526
- DOI: 10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.299
The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of multiple decontamination procedures for salivary contamination after curing of a universal adhesive on dentin bond strength according to its etch modes.
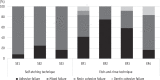
Materials and methods: Forty-two extracted bovine incisors were trimmed by exposing the labial dentin surfaces and embedded in cylindrical molds. A universal adhesive (All-Bond Universal, Bisco) was used. The teeth were randomly divided into groups according to etch mode and decontamination procedure. The adhesive was applied according to the manufacturer's instructions for a given etch mode. With the exception of the control groups, the cured adhesive was contaminated with saliva for 20 sec. In the self-etch group, the teeth were divided into three groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive. In the etch-and-rinse group, the teeth were divided into four groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive. A composite resin (Filtek Z350XT, 3M ESPE) was used for filling and was cured on the treated surfaces. Shear bond strength was measured, and failure modes were evaluated. The data were subjected to one-way analysis of variation and Tukey's HSD test.
Results: The etch-and-rinse subgroup that was decontaminated by rinse, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive showed a significantly higher bond strength.
Conclusions: When salivary contamination occurs after curing of the universal adhesive, additional etching improves the bond strength to dentin.
Keywords: Salivary contamination; Shear bond strength; Universal adhesive.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of saliva contamination and decontamination procedures on shear bond strength of self-etch dentine bonding systems: An in vitro study.J Conserv Dent. 2010 Apr;13(2):71-5. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.66714. J Conserv Dent. 2010. PMID: 20859478 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of saliva decontamination procedures on shear bond strength of a one-step adhesive system.Niger J Clin Pract. 2017 Sep;20(9):1201-1205. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.187325. Niger J Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 29072247
-
Effect of decontamination procedures on marginal and internal adaptation in saliva-contaminated composite resin restorations.Gen Dent. 2022 May-Jun;70(3):22-26. Gen Dent. 2022. PMID: 35467539
-
Effect of saliva contamination on the microshear bond strength of one-step self-etching adhesive systems to dentin.Oper Dent. 2006 Jan-Feb;31(1):127-34. doi: 10.2341/04-206. Oper Dent. 2006. PMID: 16536204 Clinical Trial.
-
Status of decontamination methods after using dentin adhesion inhibitors on indirect restorations: An integrative review of 19 publications.Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021 Nov;57:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2021.08.001. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021. PMID: 34522239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive glass ceramic can improve the bond strength of sealant/enamel?Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2019 Aug;20(4):325-331. doi: 10.1007/s40368-018-0409-x. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2019. PMID: 30903613
-
Comparative evaluation of different methods of saliva decontamination on microshear bond strength of composite to composite: An in vitro study.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2025 Jun 27;22:27. doi: 10.4103/drj.drj_736_23. eCollection 2025. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2025. PMID: 40655899 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity of Light-Cured Dental Materials according to Different Sample Preparation Methods.Materials (Basel). 2017 Mar 14;10(3):288. doi: 10.3390/ma10030288. Materials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28772647 Free PMC article.
-
Shear Bond Strength of Metal Brackets to Porcelain Using a Universal Adhesive.Med Arch. 2018 Dec;72(6):425-429. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2018.72.425-429. Med Arch. 2018. PMID: 30814774 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric materials and films in dentistry: An overview.J Adv Res. 2018 May 3;14:25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.05.001. eCollection 2018 Nov. J Adv Res. 2018. PMID: 30364755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hiraishi N, Kitasako Y, Nikaido T, Nomura S, Burrow MF, Tagami J. Effect of artificial saliva contamination on pH value change and dentin bond strength. Dent Mater. 2003;19:429–434. - PubMed
-
- Park JW, Lee KC. The influence of salivary contamination on shear bond strength of dentin adhesive systems. Oper Dent. 2004;29:437–442. - PubMed
-
- Yoo HM, Oh TS, Pereira PN. Effect of saliva contamination on the microshear bond strength of one-step self-etching adhesive systems to dentin. Oper Dent. 2006;31:127–134. - PubMed
-
- Sattabanasuk V, Shimada Y, Tagami J. Effects of saliva contamination on dentin bond strength using all-in-one adhesives. J Adhes Dent. 2006;8:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Johnson ME, Burgess JO, Hermesch CB, Buikema DJ. Saliva contamination of dentin bonding agents. Oper Dent. 1994;19:205–210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources