Gelsolin-Like Domain 3 Plays Vital Roles in Regulating the Activities of the Lily Villin/Gelsolin/Fragmin Superfamily
- PMID: 26587673
- PMCID: PMC4654503
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143174
Gelsolin-Like Domain 3 Plays Vital Roles in Regulating the Activities of the Lily Villin/Gelsolin/Fragmin Superfamily
Abstract
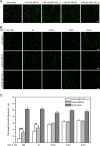
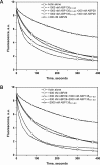
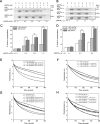
The villin/gelsolin/fragmin superfamily is a major group of Ca2+-dependent actin-binding proteins (ABPs) involved in various cellular processes. Members of this superfamily typically possess three or six tandem gelsolin-like (G) domains, and each domain plays a distinct role in actin filament dynamics. Although the activities of most G domains have been characterized, the biochemical function of the G3 domain remains poorly understood. In this study, we carefully compared the detailed biochemical activities of ABP29 (a new member of this family that contains the G1-G2 domains of lily ABP135) and ABP135G1-G3 (which contains the G1-G3 domains of lily ABP135). In the presence of high Ca2+ levels in vitro (200 and 10 μM), ABP135G1-G3 exhibited greater actin severing and/or depolymerization and nucleating activities than ABP29, and these proteins had similar actin capping activities. However, in the presence of low levels of Ca2+ (41 nM), ABP135G1-G3 had a weaker capping activity than ABP29. In addition, ABP29 inhibited F-actin depolymerization, as shown by dilution-mediated depolymerization assay, differing from the typical superfamily proteins. In contrast, ABP135G1-G3 accelerated F-actin depolymerization. All of these results demonstrate that the G3 domain plays specific roles in regulating the activities of the lily villin/gelsolin/fragmin superfamily proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
ACTIN BINDING PROTEIN 29 from Lilium pollen plays an important role in dynamic actin remodeling.Plant Cell. 2007 Jun;19(6):1930-46. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048413. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17586658 Free PMC article.
-
Domain structure in actin-binding proteins: expression and functional characterization of truncated severin.J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):665-76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.665. J Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1847147 Free PMC article.
-
The isolated sixth gelsolin repeat and headpiece domain of villin bundle F-actin in the presence of calcium and are linked by a 40-residue unstructured sequence.Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 26;46(25):7488-96. doi: 10.1021/bi700110v. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17547371 Free PMC article.
-
Gelsolin: the tail of a molecular gymnast.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013 Jul;70(7):360-84. doi: 10.1002/cm.21117. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 23749648 Review.
-
Novel inter-domain Ca2+-binding site in the gelsolin superfamily protein fragmin.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2020 Mar;41(1):153-162. doi: 10.1007/s10974-019-09571-5. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2020. PMID: 31863323 Review.
Cited by
-
GhVLN4 is involved in cell elongation via regulation of actin organization.Planta. 2017 Oct;246(4):687-700. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2723-7. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Planta. 2017. PMID: 28647813
-
Actin Cytoskeleton as Actor in Upstream and Downstream of Calcium Signaling in Plant Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 20;20(6):1403. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061403. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30897737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun H, Yamamoto M, Mejillano M, Yin HL (1999) Gelsolin, a multifunctional actin regulatory protein. J Biol Chem 274: 33179–33182. - PubMed
-
- Mcgough AM, Staiger CJ, Min JK, Simonetti KD (2003) The gelsolin family of actin regulatory proteins: Modular structures, versatile functions. FEBS Letters 552: 75–81. - PubMed
-
- Kwiatkowski DJ, Stossel TP, Orkin SH, Mole JE, Colten HR, Yin HL (1986) Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature 323: 455–458. - PubMed
-
- Burtnick LD, Koepf EK, Grimes J, Jones EY, Stuart DI, McLaughlin PJ, et al. (1997) The crystal structure of plasma gelsolin: Implications for actin severing, capping, and nucleation. Cell 90: 661–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

