Racial Differences in Survival of Incident Home Hemodialysis and Kidney Transplant Patients
- PMID: 26588010
- PMCID: PMC4873468
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001005
Racial Differences in Survival of Incident Home Hemodialysis and Kidney Transplant Patients
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have indicated that patients on maintenance hemodialysis have worse survival compared with kidney transplant (KTx) recipients. However, none of these studies have compared mortality of the US patients using alternative dialysis modalities such as home hemodialysis (HHD) with KTx recipients.
Methods: Comparing patients who started HHD with those who received kidney transplantation in the United States between 2007 and 2011, we created a 1:1 propensity score-matched cohort of 4000 patients and examined the association between treatment modality and all-cause mortality using Cox proportional hazard models.
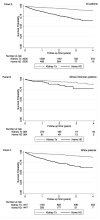
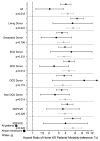
Results: The mean ± SD age of the propensity score-matched HHD and KTx patients at baseline were 54 ± 15 years and 54 ± 14 years, 65% were men (both groups), 70% and 72% of patients were whites, and 19% were African American (both groups), respectively. Over 5 years of follow-up, HHD patients had 4 times higher mortality risk compared with KTx recipients in the entire patient population (hazard ratio [HR], 4.06; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 3.27-5.04); total event number, 411), and similar difference was found across each race stratum. However, during the first year of therapy, although the white HHD patients had higher mortality risk (HR, 4.21; 95% CI, 3.10-5.73; total event number, 332) compared with their KTx counterparts, there was no significant difference in mortality risk between African American HHD and KTx patients (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 0.77-3.39; total event number, 55). This result was consistent across different types of kidney donors.
Conclusions: The HHD patients appear to have 4 times higher mortality compared with KTx recipients regardless of the type of kidney donor. Further studies are needed to understand the reasons underlying racial differenes during the first year of therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Schnuelle P, Lorenz D, Trede M, Van Der Woude FJ. Impact of renal cadaveric transplantation on survival in end-stage renal failure: evidence for reduced mortality risk compared with hemodialysis during long-term follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9(11):2135–2141. - PubMed
-
- Port FK, Wolfe RA, Mauger EA, Berling DP, Jiang K. Comparison of survival probabilities for dialysis patients vs cadaveric renal transplant recipients. JAMA. 1993;270(11):1339–1343. - PubMed
-
- Ojo AO, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Mauger EA, Williams L, Berling DP. Comparative mortality risks of chronic dialysis and cadaveric transplantation in black end-stage renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;24(1):59–64. - PubMed
-
- Rabbat CG, Thorpe KE, Russell JD, Churchill DN. Comparison of mortality risk for dialysis patients and cadaveric first renal transplant recipients in Ontario, Canada. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11(5):917–922. - PubMed
-
- Meier-Kriesche HU, Ojo AO, Port FK, Arndorfer JA, Cibrik DM, Kaplan B. Survival improvement among patients with end-stage renal disease: trends over time for transplant recipients and wait-listed patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(6):1293–1296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

