Stretching Impacts Inflammation Resolution in Connective Tissue
- PMID: 26588184
- PMCID: PMC5222602
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25263
Stretching Impacts Inflammation Resolution in Connective Tissue
Abstract
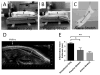
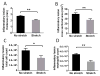
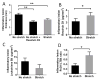
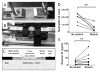
Acute inflammation is accompanied from its outset by the release of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), including resolvins, that orchestrate the resolution of local inflammation. We showed earlier that, in rats with subcutaneous inflammation of the back induced by carrageenan, stretching for 10 min twice daily reduced inflammation and improved pain, 2 weeks after carrageenan injection. In this study, we hypothesized that stretching of connective tissue activates local pro-resolving mechanisms within the tissue in the acute phase of inflammation. In rats injected with carrageenan and randomized to stretch versus no stretch for 48 h, stretching reduced inflammatory lesion thickness and neutrophil count, and increased resolvin (RvD1) concentrations within lesions. Furthermore, subcutaneous resolvin injection mimicked the effect of stretching. In ex vivo experiments, stretching of connective tissue reduced the migration of neutrophils and increased tissue RvD1 concentration. These results demonstrate a direct mechanical impact of stretching on inflammation-regulation mechanisms within connective tissue.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
C.N.S. is an inventor on patents [resolvins] assigned to BWH and licensed to Resolvyx Pharmaceuticals. C.N.S. is a scientific founder of Resolvyx Pharmaceuticals and owns equity in the company. C.N.S.’ interests were reviewed and are managed by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies.
Figures
References
-
- Bhattacharyya S, Tobacman JK. Molecular signature of kappa-carrageenan mimics chondroitin-4-sulfate and dermatan sulfate and enables interaction with arylsulfatase B. J Nutr Biochem. 2012;23(9):1058–1063. - PubMed
-
- Bouffard N, Cutroneo K, Badger G, White S, Buttolph T, Ehrlich H, Stevens-Tuttle D, Langevin H. Tissue stretch decreases soluble TGF-beta1 and type-1 procollagen in mouse subcutaneous connective tissue: Evidence from ex vivo and in vivo models. Journal of cellular physiology. 2008;214(2):389–395. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cholkar K, Trinh HM, Vadlapudi AD, Wang Z, Pal D, Mitra AK. Interaction Studies of Resolvin E1 Analog (RX-10045) with Efflux Transporters. Journal of ocular pharmacology and therapeutics : the official journal of the Association for Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2015;31(4):248–255. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

