RAN Translation in Huntington Disease
- PMID: 26590344
- PMCID: PMC4684947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.10.038
RAN Translation in Huntington Disease
Abstract
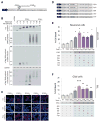
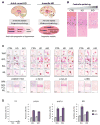
Huntington disease (HD) is caused by a CAG ⋅ CTG expansion in the huntingtin (HTT) gene. While most research has focused on the HTT polyGln-expansion protein, we demonstrate that four additional, novel, homopolymeric expansion proteins (polyAla, polySer, polyLeu, and polyCys) accumulate in HD human brains. These sense and antisense repeat-associated non-ATG (RAN) translation proteins accumulate most abundantly in brain regions with neuronal loss, microglial activation and apoptosis, including caudate/putamen, white matter, and, in juvenile-onset cases, also the cerebellum. RAN protein accumulation and aggregation are length dependent, and individual RAN proteins are toxic to neural cells independent of RNA effects. These data suggest RAN proteins contribute to HD and that therapeutic strategies targeting both sense and antisense genes may be required for efficacy in HD patients. This is the first demonstration that RAN proteins are expressed across an expansion located in an open reading frame and suggests RAN translation may also contribute to other polyglutamine diseases.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No other authors have conflicts.
Figures



References
-
- Bates G, Tabrizi SJ, Jones L, editors. Huntington’s Disease. 4. Oxford University Press; 2014.
-
- Björkqvist M, Wild EJ, Tabrizi SJ. Harnessing immune alterations in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron. 2009;64:21–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

