Fatal coma in a young adult due to late-onset urea cycle deficiency presenting with a prolonged seizure: a case report
- PMID: 26593089
- PMCID: PMC4655488
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-015-0741-2
Fatal coma in a young adult due to late-onset urea cycle deficiency presenting with a prolonged seizure: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Unexplained hyperammonemic coma in adults can be a medical dilemma in the absence of triggering factors and known comorbidities. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency presents most commonly with hyperammonemic coma. Although a rare disorder, ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency is the most common of the urea cycle disorders, which can occur both in children, and less commonly, in adults. The urea cycle disorder is usually acquired as an X-linked trait, and very rarely, similar to our reported case, may be acquired as a "new" mutation. Mutations that lead to later-onset presentations may lead to life-threatening disease and may be unrecognized, particularly when the first clinical symptoms occur in adulthood.
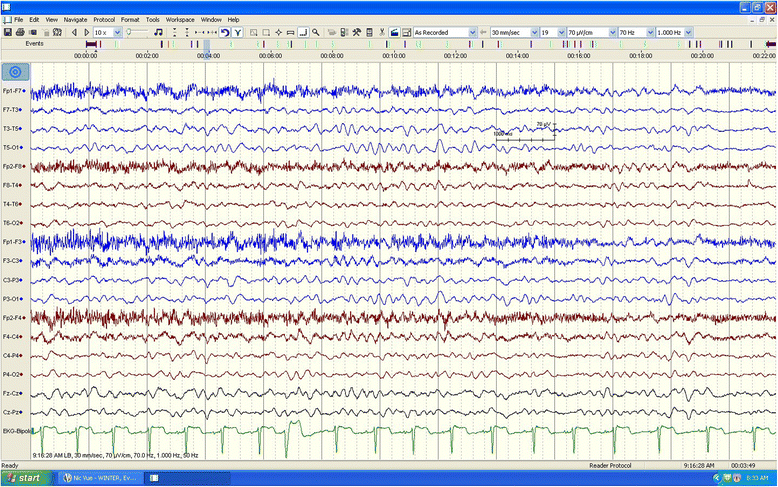
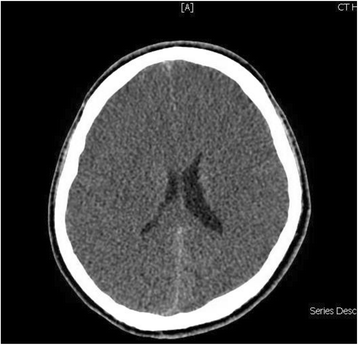
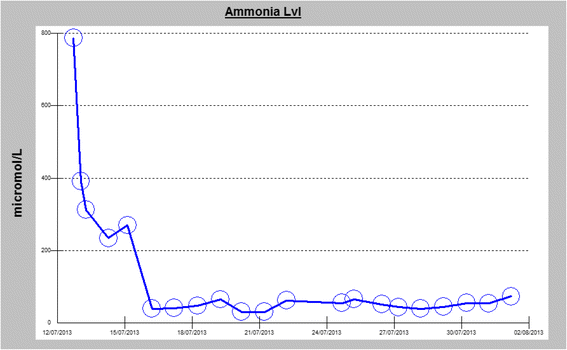
Case presentation: We report the case of a previously healthy 17-year-old white man who developed a prolonged seizure and a rapid decline in mental status leading to coma over a 3-day period. Analysis of the OTC gene showed a 119G variant, which was identified in exon 2 of the OTC gene by sequencing.
Conclusions: A diagnosis of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency should be considered in adult patients who present with unexplained hyperammonemic coma and for all adult patients presenting with cryptogenic new-onset seizure and laboratory finding of elevated blood ammonia levels. This reported case highlights the importance of early recognition of this potentially reversible cause of life-threatening encephalopathy, as timely recognition and appropriate treatment can be lifesaving.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas GH. High male:female ratio of germ-line mutations: an alternative explanation for postulated gestational lethality in males in X-linked dominant disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;58:1364–8. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1915043/. Accessed 20 April 2015. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

