MIG-seq: an effective PCR-based method for genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using the next-generation sequencing platform
- PMID: 26593239
- PMCID: PMC4655332
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16963
MIG-seq: an effective PCR-based method for genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using the next-generation sequencing platform
Abstract
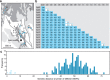
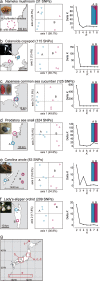
Restriction-enzyme (RE)-based next-generation sequencing methods have revolutionized marker-assisted genetic studies; however, the use of REs has limited their widespread adoption, especially in field samples with low-quality DNA and/or small quantities of DNA. Here, we developed a PCR-based procedure to construct reduced representation libraries without RE digestion steps, representing de novo single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery, and its genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Using multiplexed inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) primers, thousands of genome-wide regions were amplified effectively from a wide variety of genomes, without prior genetic information. We demonstrated: 1) Mendelian gametic segregation of the discovered variants; 2) reproducibility of genotyping by checking its applicability for individual identification; and 3) applicability in a wide variety of species by checking standard population genetic analysis. This approach, called multiplexed ISSR genotyping by sequencing, should be applicable to many marker-assisted genetic studies with a wide range of DNA qualities and quantities.
Figures

References
-
- Davey J. W. et al. Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 499–510 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Altshuler D. et al. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature 407, 513–516 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Van Tassell C. P. et al. SNP discovery and allele frequency estimation by deep sequencing of reduced representation libraries. Nat. Methods 5, 247–252 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

