5' UTR m(6)A Promotes Cap-Independent Translation
- PMID: 26593424
- PMCID: PMC4695625
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.012
5' UTR m(6)A Promotes Cap-Independent Translation
Abstract
Protein translation typically begins with the recruitment of the 43S ribosomal complex to the 5' cap of mRNAs by a cap-binding complex. However, some transcripts are translated in a cap-independent manner through poorly understood mechanisms. Here, we show that mRNAs containing N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) in their 5' UTR can be translated in a cap-independent manner. A single 5' UTR m(6)A directly binds eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3), which is sufficient to recruit the 43S complex to initiate translation in the absence of the cap-binding factor eIF4E. Inhibition of adenosine methylation selectively reduces translation of mRNAs containing 5'UTR m(6)A. Additionally, increased m(6)A levels in the Hsp70 mRNA regulate its cap-independent translation following heat shock. Notably, we find that diverse cellular stresses induce a transcriptome-wide redistribution of m(6)A, resulting in increased numbers of mRNAs with 5' UTR m(6)A. These data show that 5' UTR m(6)A bypasses 5' cap-binding proteins to promote translation under stresses.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

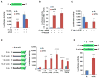

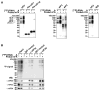
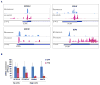
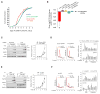
References
-
- Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–206. - PubMed
-
- Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N. eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:913–963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

