Multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of prostate cancer
- PMID: 26594835
- PMCID: PMC7511979
- DOI: 10.3322/caac.21333
Multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of prostate cancer
Abstract
Imaging has traditionally played a minor role in the diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer. However, recent controversies generated by the use of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening followed by random biopsy have encouraged the development of new imaging methods for prostate cancer. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) has emerged as the imaging method best able to detect clinically significant prostate cancers and to guide biopsies. Here, the authors explain what mpMRI is and how it is used clinically, especially with regard to high-risk populations, and we discuss the impact of mpMRI on treatment decisions for men with prostate cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:326-336. © 2015 American Cancer Society.
Keywords: active surveillance; high risk; multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); prostate cancer.
© 2015 American Cancer Society.
Figures
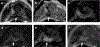
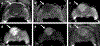
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2014. Atlanta, GA; American Cancer Society; 2014.
-
- Moyer VA; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for prostate cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2012; 157:120–135. - PubMed
-
- Stamey TA, McNeal JE, Yemoto CM, Sigal BM, Johnstone IM. Biological determinants of cancer progression in men with prostate cancer. JAMA. 1999;281:1395–1400. - PubMed
-
- Ploussard G, Epstein JI, Montironi R, et al. The contemporary concept of significant versus insignificant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2011;60:291–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

