Thyroglobulin From Molecular and Cellular Biology to Clinical Endocrinology
- PMID: 26595189
- PMCID: PMC4740344
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2015-1090
Thyroglobulin From Molecular and Cellular Biology to Clinical Endocrinology
Abstract
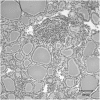
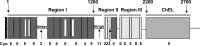
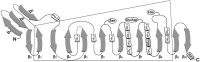
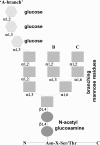
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a vertebrate secretory protein synthesized in the thyrocyte endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it acquires N-linked glycosylation and conformational maturation (including formation of many disulfide bonds), leading to homodimerization. Its primary functions include iodide storage and thyroid hormonogenesis. Tg consists largely of repeating domains, and many tyrosyl residues in these domains become iodinated to form monoiodo- and diiodotyrosine, whereas only a small portion of Tg structure is dedicated to hormone formation. Interestingly, evolutionary ancestors, dependent upon thyroid hormone for development, synthesize thyroid hormones without the complete Tg protein architecture. Nevertheless, in all vertebrates, Tg follows a strict pattern of region I, II-III, and the cholinesterase-like (ChEL) domain. In vertebrates, Tg first undergoes intracellular transport through the secretory pathway, which requires the assistance of thyrocyte ER chaperones and oxidoreductases, as well as coordination of distinct regions of Tg, to achieve a native conformation. Curiously, regions II-III and ChEL behave as fully independent folding units that could function as successful secretory proteins by themselves. However, the large Tg region I (bearing the primary T4-forming site) is incompetent by itself for intracellular transport, requiring the downstream regions II-III and ChEL to complete its folding. A combination of nonsense mutations, frameshift mutations, splice site mutations, and missense mutations in Tg occurs spontaneously to cause congenital hypothyroidism and thyroidal ER stress. These Tg mutants are unable to achieve a native conformation within the ER, interfering with the efficiency of Tg maturation and export to the thyroid follicle lumen for iodide storage and hormonogenesis.
Figures









References
-
- Pharoah PO, Buttfield IH, Hetzel BS. Neurological damage to the fetus resulting from severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy. Lancet. 1971;1:308–310. - PubMed
-
- Frati L, Bilstad J, Edelhoch H, Rall JE, Salvatore G. Biosynthesis of the 27 S thyroid iodoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974;162:126–134. - PubMed
-
- Novinec M, Kordis D, Turk V, Lenarcic B. Diversity and evolution of the thyroglobulin type-1 domain superfamily. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;23:744–755. - PubMed
-
- Takagi Y, Omura T, Go M. Evolutionary origin of thyroglobulin by duplication of esterase gene. FEBS Lett. 1991;282:17–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

