CRISPR-Cas9-based target validation for p53-reactivating model compounds
- PMID: 26595461
- PMCID: PMC4910870
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1965
CRISPR-Cas9-based target validation for p53-reactivating model compounds
Abstract
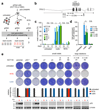
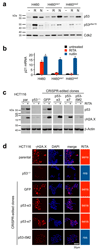
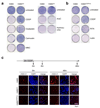
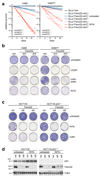
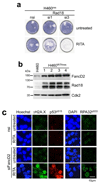
Inactivation of the p53 tumor suppressor by Mdm2 is one of the most frequent events in cancer, so compounds targeting the p53-Mdm2 interaction are promising for cancer therapy. Mechanisms conferring resistance to p53-reactivating compounds are largely unknown. Here we show using CRISPR-Cas9-based target validation in lung and colorectal cancer that the activity of nutlin, which blocks the p53-binding pocket of Mdm2, strictly depends on functional p53. In contrast, sensitivity to the drug RITA, which binds the Mdm2-interacting N terminus of p53, correlates with induction of DNA damage. Cells with primary or acquired RITA resistance display cross-resistance to DNA crosslinking compounds such as cisplatin and show increased DNA cross-link repair. Inhibition of FancD2 by RNA interference or pharmacological mTOR inhibitors restores RITA sensitivity. The therapeutic response to p53-reactivating compounds is therefore limited by compound-specific resistance mechanisms that can be resolved by CRISPR-Cas9-based target validation and should be considered when allocating patients to p53-reactivating treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

