Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance
- PMID: 26595536
- PMCID: PMC4821713
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2015.247
Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance
Abstract
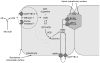
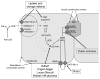
Inherited disorders of hyperbilirubinemia may be caused by increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin clearance. Reduced hepatic bilirubin clearance can be due to defective (i) unconjugated bilirubin uptake and intrahepatic storage, (ii) conjugation of glucuronic acid to bilirubin (e.g., Gilbert syndrome, Crigler-Najjar syndrome, Lucey-Driscoll syndrome, breast milk jaundice), (iii) bilirubin excretion into bile (Dubin-Johnson syndrome), or (iv) conjugated bilirubin re-uptake (Rotor syndrome). In this review, the molecular mechanisms and clinical manifestations of these conditions are described, as well as current approaches to diagnosis and therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- London IM, West R, Shemin D, Rittenberg D. On the origin of bile pigment in normal man. J Biol Chem. 1950;184:351–8. - PubMed
-
- Watchko JF, Tiribelli C. Bilirubin-induced neurologic damage--mechanisms and management approaches. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2021–30. - PubMed
-
- Sorrentino D, Berk PD. Mechanistic aspects of hepatic bilirubin uptake. Semin Liver Dis. 1988;8:119–36. - PubMed
-
- Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ. Organic anion transporting polypeptides of the OATP/SLC21 family: phylogenetic classification as OATP/SLCO superfamily, new nomenclature and molecular/functional properties. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:653–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

