Immune activation caused by vascular oxidation promotes fibrosis and hypertension
- PMID: 26595812
- PMCID: PMC4701546
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI80761
Immune activation caused by vascular oxidation promotes fibrosis and hypertension
Erratum in
-
Immune activation caused by vascular oxidation promotes fibrosis and hypertension.J Clin Invest. 2016 Apr 1;126(4):1607. doi: 10.1172/JCI87425. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27035819 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
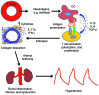
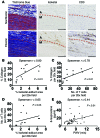
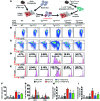
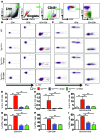
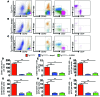
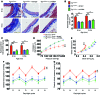
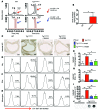
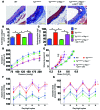
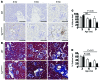
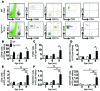
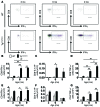
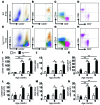
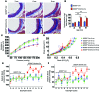
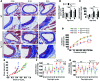
Vascular oxidative injury accompanies many common conditions associated with hypertension. In the present study, we employed mouse models with excessive vascular production of ROS (tg(sm/p22phox) mice, which overexpress the NADPH oxidase subunit p22(phox) in smooth muscle, and mice with vascular-specific deletion of extracellular SOD) and have shown that these animals develop vascular collagen deposition, aortic stiffening, renal dysfunction, and hypertension with age. T cells from tg(sm/p22phox) mice produced high levels of IL-17A and IFN-γ. Crossing tg(sm/p22phox) mice with lymphocyte-deficient Rag1(-/-) mice eliminated vascular inflammation, aortic stiffening, renal dysfunction, and hypertension; however, adoptive transfer of T cells restored these processes. Isoketal-protein adducts, which are immunogenic, were increased in aortas, DCs, and macrophages of tg(sm/p22phox) mice. Autologous pulsing with tg(sm/p22phox) aortic homogenates promoted DCs of tg(sm/p22phox) mice to stimulate T cell proliferation and production of IFN-γ, IL-17A, and TNF-α. Treatment with the superoxide scavenger tempol or the isoketal scavenger 2-hydroxybenzylamine (2-HOBA) normalized blood pressure; prevented vascular inflammation, aortic stiffening, and hypertension; and prevented DC and T cell activation. Moreover, in human aortas, the aortic content of isoketal adducts correlated with fibrosis and inflammation severity. Together, these results define a pathway linking vascular oxidant stress to immune activation and aortic stiffening and provide insight into the systemic inflammation encountered in common vascular diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hypertension: Oxidative stress and immune activation in hypertension.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Jan;12(1):4. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.200. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26639988 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL039006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL039006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32HL124972-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201400010C/PHS HHS/United States
- HHSN268201400010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108701/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL121671/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL58000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042527/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL105294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL058000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K08HL121671/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117913/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL108701/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119968/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI108906/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL124972/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125865/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088975/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL130497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

