Kill-painting of hypoxic tumours in charged particle therapy
- PMID: 26596243
- PMCID: PMC4657060
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17016
Kill-painting of hypoxic tumours in charged particle therapy
Abstract
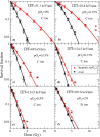
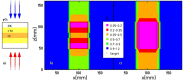
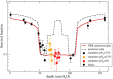
Solid tumours often present regions with severe oxygen deprivation (hypoxia), which are resistant to both chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Increased radiosensitivity as a function of the oxygen concentration is well described for X-rays. It has also been demonstrated that radioresistance in anoxia is reduced using high-LET radiation rather than conventional X-rays. However, the dependence of the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER) on radiation quality in the regions of intermediate oxygen concentrations, those normally found in tumours, had never been measured and biophysical models were based on extrapolations. Here we present a complete survival dataset of mammalian cells exposed to different ions in oxygen concentration ranging from normoxia (21%) to anoxia (0%). The data were used to generate a model of the dependence of the OER on oxygen concentration and particle energy. The model was implemented in the ion beam treatment planning system to prescribe uniform cell killing across volumes with heterogeneous radiosensitivity. The adaptive treatment plans have been validated in two different accelerator facilities, using a biological phantom where cells can be irradiated simultaneously at three different oxygen concentrations. We thus realized a hypoxia-adapted treatment plan, which will be used for painting by voxel of hypoxic tumours visualized by functional imaging.
Figures





References
-
- Hanahan D. & Weinberg R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wilson W. R. & Hay M. P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11, 393–410 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Brown J. M. & Wilson W. R. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 437–447 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Schardt D., Elsässer T. & Schulz-Ertner D. Heavy-ion tumor therapy: Physical and radiobiological benefits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 383–425 (2010).
-
- Kamada T. et al. Carbon ion radiotherapy in Japan: an assessment of 20 years of clinical experience. Lancet Oncol 16, e93–e100 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

