In Vitro Effects of Polyphosphate against Prevotella intermedia in Planktonic Phase and Biofilm
- PMID: 26596937
- PMCID: PMC4750699
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01861-15
In Vitro Effects of Polyphosphate against Prevotella intermedia in Planktonic Phase and Biofilm
Abstract
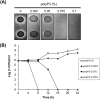
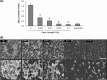
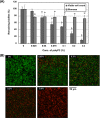
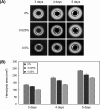
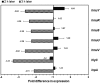
Polyphosphate (polyP) has gained a wide interest in the food industry due to its potential as a decontaminating agent. In this study, we examined the effect of sodium tripolyphosphate (polyP3; Na5P3O10) against planktonic and biofilm cells of Prevotella intermedia, a major oral pathogen. The MIC of polyP3 against P. intermedia ATCC 49046 determined by agar dilution method was 0.075%, while 0.05% polyP3 was bactericidal against P. intermedia in time-kill analysis performed using liquid medium. A crystal violet binding assay for the assessment of biofilm formation by P. intermedia showed that sub-MICs of polyP3 significantly decreased biofilm formation. Under the scanning electron microscope, decreased numbers of P. intermedia cells forming the biofilms were observed when the bacterial cells were incubated with 0.025% or higher concentrations of polyP3. Assessment of biofilm viability with LIVE/DEAD staining and viable cell count methods showed that 0.05% or higher concentrations of polyP3 significantly decreased the viability of the preformed biofilms in a concentration-dependent manner. The zone sizes of alpha-hemolysis formed on horse blood agar produced by P. intermedia were decreased in the presence of polyP3. The expression of the genes encoding hemolysins and the genes of the hemin uptake (hmu) locus was downregulated by polyP3. Collectively, our results show that polyP is an effective antimicrobial agent against P. intermedia in biofilms as well as planktonic phase, interfering with the process of hemin acquisition by the bacterium.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Sodium Tripolyphosphate on Oral Commensal and Pathogenic Bacteria.Pol J Microbiol. 2019;68(2):263-268. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2019-029. Pol J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31257792 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm effects of iron chelators against Prevotella intermedia.J Med Microbiol. 2013 Sep;62(Pt 9):1307-1316. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.053553-0. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Med Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23329319
-
In vitro effects of N-acetyl cysteine alone and in combination with antibiotics on Prevotella intermedia.J Microbiol. 2015 May;53(5):321-9. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-4500-2. Epub 2015 May 3. J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25935303
-
The effects of tetracycline, minocycline, doxycycline and ofloxacin on Prevotella intermedia biofilm.Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2006 Dec;21(6):366-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2006.00305.x. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17064394
-
Inhibitory effects of lactoferrin on growth and biofilm formation of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Prevotella intermedia.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Aug;53(8):3308-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01688-08. Epub 2009 May 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19451301 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antibacterial effects of sodium tripolyphosphate against Porphyromonas species associated with periodontitis of companion animals.J Vet Sci. 2019 Jul;20(4):e33. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.e33. J Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31364318 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of sodium long chain polyphosphate as a potential growth promoter in broilers.J Anim Sci Technol. 2021 Nov;63(6):1286-1300. doi: 10.5187/jast.2021.e110. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Anim Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34957444 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Sodium Tripolyphosphate on Oral Commensal and Pathogenic Bacteria.Pol J Microbiol. 2019;68(2):263-268. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2019-029. Pol J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31257792 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and phenotypic comparison of Prevotella intermedia strains possessing different virulence in vivo.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):1133-1145. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2095718. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35791444 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial effects of N-acetylcysteine against endodontic pathogens.J Microbiol. 2016 Apr;54(4):322-9. doi: 10.1007/s12275-016-5534-9. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27033208
References
-
- Polson AM, Garrett S, Stoller NH, Bandt CL, Hanes PJ, Killoy WJ, Southard GL, Duke SP, Bogle GC, Drisko CH, Friesen LR. 1997. Multi-center comparative evaluation of subgingivally delivered sanguinarine and doxycycline in the treatment of periodontitis. II. Clinical results. J Periodontol 68:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

