Effects of rosuvastatin and/or β-carotene on non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats
- PMID: 26600855
- PMCID: PMC4623617
Effects of rosuvastatin and/or β-carotene on non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats
Abstract
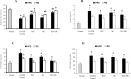
The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has markedly increased, especially in patients exhibit one or more features of the metabolic syndrome. This study investigates the effect of rosuvastatin (RSV) and/or β-carotene (βC) in NAFLD-induced rats. Rats were classified into nine groups; normal (I), NAFLD-induced with high-fat diet (HFD; II), NAFLD switched to regular diet (RD; III), NAFLD-HFD or NAFLD-RD treated with RSV (IV, V), βC (VI, VII) or both RSV+βC (VIII, IX), respectively. After four weeks, rats were sacrificed to obtain serum samples and liver tissues. Liver histology, lipid profile, liver oxidative stress markers, and adipocytokines were measured. Liver sections of rats with NAFLD-HFD revealed steatosis, lose of hepatic architecture, inflammation and hepatocyte vacuolation with high percentage of cell fibrosis. Serum levels of ALT, AST, ALP, gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) and lipid profile (triglycerides, cholesterol, LDL and VLDL) were significantly increased (P<0.05) compared with normal. Also, hepatic malondialdehyde level and serum leptin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) were increased. Meanwhile, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, GSH content in liver, serum HDL and adiponectin were decreased (P<0.05) vs normal. These changes were observed to a lesser extent in NAFLD-RD group. Administration of RSV or/and βC almost improved all previously mentioned parameters. Moreover, hepatic steatosis was decreased and inflammation was markedly ameliorated with reduction of TNF-α and TGF-β. These results were more pronounced in the groups VIII and IX vs each drug alone. In conclusion RSV and βC could be beneficial for the treatment and prevention of NAFLD. Combined RSV with βC is more effective than RSV alone.
Keywords: NAFLD; Oxidative stress; Rosuvastatin; TGF-β1; TNF-α; β-carotene.
Figures


References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi KN, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology and the American Gastroenterological Association. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;142:1592–1609. - PubMed
-
- Bellentani S, Scaglioni F, Marino M, Bedogni G. Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis. 2010;28:155–161. - PubMed
-
- Williams CD, Stengel J, Asike MI, Torres DM, Shaw J, Contreras M, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:124–131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
