Alcoholic hepatitis: The pivotal role of Kupffer cells
- PMID: 26600966
- PMCID: PMC4644891
- DOI: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.90
Alcoholic hepatitis: The pivotal role of Kupffer cells
Abstract
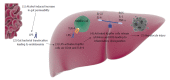
Kupffer cells play a central role in the pathogenesis of alcoholic hepatitis (AH). It is believed that alcohol increases the gut permeability that results in raised levels of serum endotoxins containing lipopolysaccharides (LPS). LPS binds to LPS-binding proteins and presents it to a membrane glycoprotein called CD14, which then activates Kupffer cells via a receptor called toll-like receptor 4. This endotoxin mediated activation of Kupffer cells plays an important role in the inflammatory process resulting in alcoholic hepatitis. There is no effective treatment for AH, although notable progress has been made over the last decade in understanding the underlying mechanism of alcoholic hepatitis. We specifically review the current research on the role of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of AH and the treatment strategies. We suggest that the imbalance between the pro-inflammatory and the anti-inflammatory process as well as the increased production of reactive oxygen species eventually lead to hepatocyte injury, the final event of alcoholic hepatitis.
Keywords: Alcoholic hepatitis; Alcoholic liver disease; Kupffer cells; Macrophages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethanol-induced sensitization to endotoxin in Kupffer cells is dependent upon oxidative stress.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Dec;29(12 Suppl):246S-50S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000191128.54871.40. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16385231
-
[Ethanol changes sensitivity of Kupffer cells to endotoxin].Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2003 Oct;38(5):415-24. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14639920 Review. Japanese.
-
Common pathogenic mechanism in development progression of liver injury caused by non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Toxicol Sci. 2007 Dec;32(5):453-68. doi: 10.2131/jts.32.453. J Toxicol Sci. 2007. PMID: 18198478 Review.
-
Role of Kupffer cells and gut-derived endotoxins in alcoholic liver injury.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000 Mar;15 Suppl:D20-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2000.02179.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000. PMID: 10759216 Review.
-
Relation of endotoxin, endotoxin binding proteins and macrophages to severe alcoholic liver injury and multiple organ failure.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Nov;29(11 Suppl):172S-179S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000189278.30237.e9. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16344605 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current Management.Alcohol Res. 2017;38(2):147-161. Alcohol Res. 2017. PMID: 28988570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Natural Phenolics in Hepatoprotection: A Mechanistic Review and Analysis of Regulatory Network of Associated Genes.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 24;10:509. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00509. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31178720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Acute or Chronic Alcohol Intake on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 10;21(24):9407. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249407. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33321885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Ameliorates Chronic Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice via AMPK and TLR-4/TGF-β1 Pathways.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 28;34(3):606-621. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2310.10003. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38111317 Free PMC article.
-
Resident macrophages of the lung and liver: The guardians of our tissues.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 30;13:1029085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1029085. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36532044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lefkowitch JH. Morphology of alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:37–53. - PubMed
-
- O’Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51:307–328. - PubMed
-
- Chedid A, Arain S, Snyder A, Mathurin P, Capron F, Naveau S. The immunology of fibrogenesis in alcoholic liver disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128:1230–1238. - PubMed
-
- Kupffer C. Ueber Sternzellen der Leber. Archiv fmikrosk Anat. 1876;12:353–358.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

