SUMOylation-Mediated Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression and Cancer
- PMID: 26601932
- PMCID: PMC4874464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.09.006
SUMOylation-Mediated Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression and Cancer
Abstract
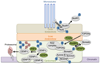
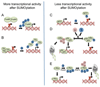
Protein conjugation with Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMOylation) has critical roles during cell cycle progression. Many important cell cycle regulators, including many oncogenes and tumor suppressors, are functionally regulated via SUMOylation. The dynamic SUMOylation pattern observed throughout the cell cycle is ensured via distinct spatial and temporal regulation of the SUMO machinery. Additionally, SUMOylation cooperates with other post-translational modifications to mediate cell cycle progression. Deregulation of these SUMOylation and deSUMOylation enzymes causes severe defects in cell proliferation and genome stability. Different types of cancer were recently shown to be dependent on a functioning SUMOylation system, a finding that could be exploited in anticancer therapies.
Keywords: SUMO; SUMOylation; cancer; cell cycle; mitosis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

