Developmental progress and current status of the Animal QTLdb
- PMID: 26602686
- PMCID: PMC4702873
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1233
Developmental progress and current status of the Animal QTLdb
Abstract
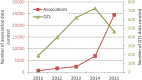
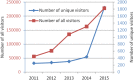
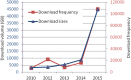
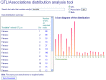
The Animal QTL Database (QTLdb; http://www.animalgenome.org/QTLdb) has undergone dramatic growth in recent years in terms of new data curated, data downloads and new functions and tools. We have focused our development efforts to cope with challenges arising from rapid growth of newly published data and end users' data demands, and to optimize data retrieval and analysis to facilitate users' research. Evidenced by the 27 releases in the past 11 years, the growth of the QTLdb has been phenomenal. Here we report our recent progress which is highlighted by addition of one new species, four new data types, four new user tools, a new API tool set, numerous new functions and capabilities added to the curator tool set, expansion of our data alliance partners and more than 20 other improvements. In this paper we present a summary of our progress to date and an outlook regarding future directions.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Hu Z.L., Dracheva S., Jang W., Maglott D., Bastiaansen J., Rothschild M.F., Reecy J.M. A QTL resource and comparison tool for pigs: PigQTLDB. Mamm. Genome. 2005;16:792–800. - PubMed
-
- Hu Z.L., Park C.A., Fritz E.R., Reecy J.M. Proceedings of the 9th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production. Leipzig: 2010. QTLdb: A comprehensive database tool building bridges between genotypes and phenotypes.
-
- Hu Z., Wu X., Reecy J. ACM Conference on Bioinformatics, Computional Biology, and Biomedicine (ACM-BCB) Chicago: 2011. QTL meta-analysis on the fly.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

