A prospective case-control study to investigate retinal microvascular changes in acute dengue infection
- PMID: 26603217
- PMCID: PMC4658599
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17183
A prospective case-control study to investigate retinal microvascular changes in acute dengue infection
Abstract
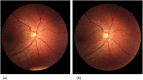
Dengue infection can affect the microcirculation by direct viral infection or activation of inflammation. We aimed to determine whether measured retinal vascular parameters were associated with acute dengue infection. Patients with acute dengue were recruited from Communicable Diseases Center, Singapore and age-gender-ethnicity matched healthy controls were selected from a population-based study. Retinal photographs were taken on recruitment and convalescence. A spectrum of quantitative retinal microvascular parameters (retinal vascular caliber, fractal dimension, tortuosity and branching angle) was measured using a semi-automated computer-based program. (Singapore I Vessel Assessment, version 3.0). We included 62 dengue patients and 127 controls. Dengue cases were more likely to have wider retinal arteriolar and venular calibers (158.3 μm vs 144.3 μm, p < 0.001; 227.7 μm vs 212.8 μm, p < 0.001; respectively), higher arteriolar and venular fractal dimensions (1.271 vs 1.249, p = 0.002; 1.268 vs. 1.230, p < 0.001, respectively), higher arteriolar and venular tortuosity (0.730 vs 0.546 [x10(4)], p < 0.001; 0.849 vs 0.658 [x10(4)], p < 0.001; respectively), compared to controls. Resolution of acute dengue coincided with decrease in retinal vascular calibers and venular fractal dimension. Dengue patients have altered microvascular network in the retina; these changes may reflect pathophysiological processes in the immune system.
Figures

References
-
- Communicable Diseases Division,Ministry of Health Singapore. Weekly Infectious Disease Bulletin (2015). Availbale at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/content/dam/moh_web/Statistics/Infectious_Disease.... (Accessed 21 March 2015).
-
- Cardier J. E. et al. Proinflammatory factors present in sera from patients with acute dengue infection induce activation and apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells: possible role of TNF-alpha in endothelial cell damage in dengue. Cytokine. 30, 359–365 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Cheung C. Y., Ikram M. K., Sabanayagam C. & Wong T. Y. Retinal microvasculature as a model to study the manifestations of hypertension. Hypertension. 60, 1094–1103 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

