Antioxidant resveratrol restores renal sodium transport regulation in SHR
- PMID: 26603454
- PMCID: PMC4673646
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12618
Antioxidant resveratrol restores renal sodium transport regulation in SHR
Abstract
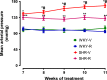
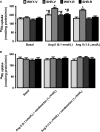
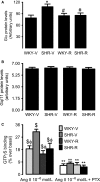
Previously we have shown that in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) renal angiotensin (Ang) II receptor (AT1R) upregulation leads to overstimulation of Na/K-ATPase by Ang II. There are reports that antioxidants can reduce oxidative stress and blood pressure (BP) in SHR, however the effect of these compounds on AT1R function remains to be determined. Therefore, we hypothesized that polyphenol antioxidant resveratrol would mitigate oxidative stress, normalize renal AT1R signaling, and reduce BP in SHR. SHR and wistar-kyoto (WKY) rats were treated with resveratrol for 8 weeks. Untreated SHR exhibited oxidative stress and enhanced renal proximal tubular Ang II-induced G-protein activation and Na/K-ATPase stimulation. Treatment of SHR with resveratrol mitigated oxidative stress, reduced BP, and normalized renal AT1R signaling. In SHR, nuclear expression of transcription factor NF-κB was increased while expression of Nrf2 was reduced. SHR also exhibited a significant decrease in renal antioxidant capacity and activities of phase II antioxidant enzymes. Resveratrol treatment of SHR abolished renal NF-κB activation, restored Nrf2-phase II antioxidant signaling and Ang II-mediated Na/K-ATPase regulation. These data show that in SHR, oxidative stress via activation of NF-κB upregulates AT1R-G-protein signaling resulting in overstimulation Na/K-ATPase which contributes to hypertension. Resveratrol, via Nrf2, activates phase II antioxidant enzymes, mitigates oxidative stress, normalizes AT1R-G-protein signaling and Na/K-ATPase regulation, and decreases BP in SHR.
Keywords: G proteins; Na/K‐ATPase; hypertension; oxidative stress; transcription factors.
© 2015 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Arinze IJ. Kawai Y. Transcriptional activation of the human Galphai2 gene promoter through nuclear factor-kappaB and antioxidant response elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:9786–9795. - PubMed
-
- Asghar M, Banday AA, Fardoun RZ. Lokhandwala MF. Hydrogen peroxide causes uncoupling of dopamine D1-like receptors from G proteins via a mechanism involving protein kinase C and G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006;40:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Banday AA. Lokhandwala MF. Loss of biphasic effect on Na/K-ATPase activity by angiotensin II involves defective angiotensin type 1 receptor-nitric oxide signaling. Hypertension. 2008;52:1099–1105. - PubMed
-
- Banday AA. Lokhandwala MF. Angiotensin II-mediated biphasic regulation of proximal tubular Na+/H+ exchanger 3 is impaired during oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2011;301:F364–F370. - PubMed
-
- Banday AA, Asghar M, Hussain T. Lokhandwala MF. Dopamine-mediated inhibition of renal Na, K-ATPase is reduced by insulin. Hypertension. 2003;41:1353–1358. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

