Diagnostic tool for red blood cell membrane disorders: Assessment of a new generation ektacytometer
- PMID: 26603718
- PMCID: PMC4811191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2015.09.001
Diagnostic tool for red blood cell membrane disorders: Assessment of a new generation ektacytometer
Abstract
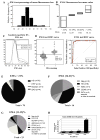
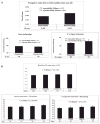
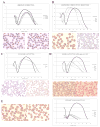
Inherited red blood cell (RBC) membrane disorders, such as hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis and hereditary ovalocytosis, result from mutations in genes encoding various RBC membrane and skeletal proteins. The RBC membrane, a composite structure composed of a lipid bilayer linked to a spectrin/actin-based membrane skeleton, confers upon the RBC unique features of deformability and mechanical stability. The disease severity is primarily dependent on the extent of membrane surface area loss. RBC membrane disorders can be readily diagnosed by various laboratory approaches that include RBC cytology, flow cytometry, ektacytometry, electrophoresis of RBC membrane proteins and genetics. The reference technique for diagnosis of RBC membrane disorders is the osmotic gradient ektacytometry. However, in spite of its recognition as the reference technique, this technique is rarely used as a routine diagnosis tool for RBC membrane disorders due to its limited availability. This may soon change as a new generation of ektacytometer has been recently engineered. In this review, we describe the workflow of the samples shipped to our Hematology laboratory for RBC membrane disorder analysis and the data obtained for a large cohort of French patients presenting with RBC membrane disorders using a newly available version of the ektacytomer.
Keywords: EMA; Ektacytometer; LoRRca; Red blood cell membrane; Spherocytosis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Mohandas N, Chasis JA, Shohet SB. The influence of membrane skeleton on red cell deformability, membrane material properties, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983;20:225–242. - PubMed
-
- Mohandas N, Chasis JA. Red blood cell deformability, membrane material properties and shape: regulation by transmembrane, skeletal and cytosolic proteins and lipids. Semin Hematol. 1993;30:171–192. - PubMed
-
- Mohandas N, Evans E. Mechanical properties of the red cell membrane in relation to molecular structure and genetic defects. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:787–818. - PubMed
-
- Mohandas N, An X. New insights into function of red cell membrane proteins and their interaction with spectrin-based membrane skeleton. Transfus Clin Biol. 2006;13:29–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

