Interferons and the Immunogenic Effects of Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 26604042
- PMCID: PMC4752403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2015.09.007
Interferons and the Immunogenic Effects of Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Much of our understanding on resistance mechanisms to conventional cancer therapies such as chemotherapy and radiation has focused on cell intrinsic properties that antagonize the detrimental effects of DNA and other cellular damage. However, it is becoming clear that the immune system and/or innate immune signaling pathways can integrate with these intrinsic mechanisms to profoundly influence treatment efficacy. In this context, recent evidence indicates that interferon (IFN) signaling has an important role in this integration by influencing immune and intrinsic/non-immune determinants of therapy response. However, IFN signaling can be both immunostimulatory and immunosuppressive, and the factors determining these outcomes in different disease settings are unclear. Here I discuss the regulation and molecular events in cancer that are associated with these dichotomous functions.
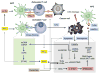
Figures
References
-
- Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. The Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. The Lancet. 2005;366:2087–2106. - PubMed
-
- Yom SS. Radiation treatment of head and neck cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2015;24:423–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

