Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics- a review
- PMID: 26604335
- PMCID: PMC4648921
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-015-1921-1
Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics- a review
Abstract
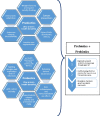
The health benefits imparted by probiotics and prebiotics as well as synbiotics have been the subject of extensive research in the past few decades. These food supplements termed as functional foods have been demonstrated to alter, modify and reinstate the pre-existing intestinal flora. They also facilitate smooth functions of the intestinal environment. Most commonly used probiotic strains are: Bifidobacterium, Lactobacilli, S. boulardii, B. coagulans. Prebiotics like FOS, GOS, XOS, Inulin; fructans are the most commonly used fibers which when used together with probiotics are termed synbiotics and are able to improve the viability of the probiotics. Present review focuses on composition and roles of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in human health. Furthermore, additional health benefits like immune-modulation, cancer prevention, inflammatory bowel disease etc. are also discussed. Graphical abstractPictorial summary of health benefits imparted by probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics.
Keywords: Cancer; Cardiovascular diseases; Intestinal disorders; Prebiotics; Probiotics; Synbiotics.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams SA, Griffin IJ, Hawthorne KM, Liang L, Gunn SK, Darlington G, Ellis KJ. A combination of prebiotic short-and long-chain inulin-type fructans enhances calcium absorption and bone mineralization in young adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82(2):471–476. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous