Using Kepler for Tool Integration in Microarray Analysis Workflows
- PMID: 26605000
- PMCID: PMC4655117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2014.05.201
Using Kepler for Tool Integration in Microarray Analysis Workflows
Abstract
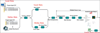
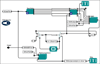
Increasing numbers of genomic technologies are leading to massive amounts of genomic data, all of which requires complex analysis. More and more bioinformatics analysis tools are being developed by scientist to simplify these analyses. However, different pipelines have been developed using different software environments. This makes integrations of these diverse bioinformatics tools difficult. Kepler provides an open source environment to integrate these disparate packages. Using Kepler, we integrated several external tools including Bioconductor packages, AltAnalyze, a python-based open source tool, and R-based comparison tool to build an automated workflow to meta-analyze both online and local microarray data. The automated workflow connects the integrated tools seamlessly, delivers data flow between the tools smoothly, and hence improves efficiency and accuracy of complex data analyses. Our workflow exemplifies the usage of Kepler as a scientific workflow platform for bioinformatics pipelines.
Keywords: AltAnalyze; Integration; Kepler; Microarray; Workflow.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Workflows for microarray data processing in the Kepler environment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 May 17;13:102. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-102. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22594911 Free PMC article.
-
Reusable, extensible, and modifiable R scripts and Kepler workflows for comprehensive single set ChIP-seq analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jul 5;17(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1125-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27377783 Free PMC article.
-
MAAMD: a workflow to standardize meta-analyses and comparison of affymetrix microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Mar 12;15:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-69. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24621103 Free PMC article.
-
The metaRbolomics Toolbox in Bioconductor and beyond.Metabolites. 2019 Sep 23;9(10):200. doi: 10.3390/metabo9100200. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 31548506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Facilitating the use of large-scale biological data and tools in the era of translational bioinformatics.Brief Bioinform. 2014 Nov;15(6):942-52. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbt055. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Brief Bioinform. 2014. PMID: 23908249 Review.
References
-
- Koschmieder A, Zimmermann K, Trissl S, Stoltmann T, Leser U. Tools for managing and analyzing microarray data. Brief Bioinform. 2012;13:46–60. - PubMed
-
- Dudoit S, Gentleman RC, Quackenbush J. Open source software for the analysis of microarray data. BioTechniques. 2003;(Suppl):45–51. - PubMed
-
- Barker A, Hemert Jv. Proc. Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics, Poland, 2007. Vol. 4967. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2008. Scientific Workflow: A Survey and Research Directions; pp. 746–753.
-
- Altintas I, Berkley C, Jaeger E, Jones M, Ludaescher B, Mock S. Kepler: An extensible system for design and execution of scientific workflows; Proc. Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management; 2004. pp. 423–424.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources