Stability-Indicating HPLC Assay for Determination of Idebenone in Pharmaceutical Forms
- PMID: 26605105
- PMCID: PMC4641926
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/835986
Stability-Indicating HPLC Assay for Determination of Idebenone in Pharmaceutical Forms
Abstract
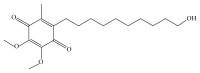
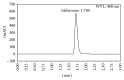
A stability-indicating method was validated for the determination in pharmaceutical forms of idebenone a coenzyme Q10-like compound. The assay was achieved by liquid chromatography analysis using a reversed-phase C18 column and a detector set at 480 nm. The optimized mobile phase consisted of isocratic flow rate at 1.0 mL/min for 3 min with methanol. The linearity of the assay was demonstrated in the range of 3.0 to 8.0 mg/mL with a correlation coefficient r (2) > 0.998. The limits of detection and quantification were 0.03 and 0.05 mg/mL, respectively. The intraday and interday precisions were less than 1.0%. Accuracy of the method ranged from 98.6 to 101.5% with RSD < 0.6%. Specificity of the assay showed no interference from tablets components and breakdown products formed by alkaline, acidic, oxidative, sunlight, and high temperature conditions. This method allows accurate and reliable determination of idebenone for drug stability assay in pharmaceutical studies.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

