Groin pain syndrome: an association of different pathologies and a case presentation
- PMID: 26605198
- PMCID: PMC4617224
- DOI: 10.11138/mltj/2015.5.3.214
Groin pain syndrome: an association of different pathologies and a case presentation
Abstract
Background: groin pain affects all types of athletes, especially soccer players. Many diseases with different etiologies may cause groin pain.
Purpose: offer a mini review of groin pain in soccer accompanied by the presentation of a case report highlighting the possible association of more clinical frameworks into the onset of groin pain syndrome, in order to recommend that clinical evaluations take into account possible associations between bone, muscle and tendon such as inguinal canal disease.
Conclusion: the multifactorial etiology of groin pain syndrome needs to be examined with a comprehensive approach, with standardized clinical evaluation based on an imaging protocol in order to evaluate all possible diseases.
Study design: Mini review- Case report (Level V).
Keywords: adductor tendinopathy; groin pain syndrome; osteitis pubis; sport hernia.
Figures
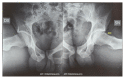
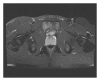

References
-
- Omar IM, Zoga AC, Kavanagh EC, et al. Athletic pubalgia and “sports hernia”: optimal MR imaging technique and findings. Radiographics. 2008;28(5):1415–1438. - PubMed
-
- Weir A. Report from the groin pain consensus conference 2014. Football Medicine Strategies for Player Care (Abstract book); 11th–12th April, 2015; London. 2015. pp. 68–69.
-
- Hölmich P, Thorborg K, Dehlendorff C, Krogsgaard K, Gluud C. Incidence and clinical presentation of groin injuries in sub-elite male soccer. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(16):1245–1250. - PubMed
-
- Engebretsen AH, Myklebust G, Holme I, Engebretsen L, Bahr R. Intrinsic risk factors for groin injuries among male soccer players: a prospective cohort study. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(10):2051–2057. - PubMed
-
- Benazzo F, Mosconi M, Zanon G, Bertani B. Groin Pain. J Sport Traumatol Rel Res. 1999;21(1):30–40.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
