Correction: Brief Parenteral Nutrition Accelerates Weight Gain, Head Growth Even in Healthy VLBWs
- PMID: 26606139
- PMCID: PMC4659585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143984
Correction: Brief Parenteral Nutrition Accelerates Weight Gain, Head Growth Even in Healthy VLBWs
Figures

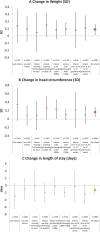
Erratum for
-
Brief parenteral nutrition accelerates weight gain, head growth even in healthy VLBWs.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 19;9(2):e88392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088392. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morisaki N, Belfort MB, McCormick MC, Mori R, Noma H, Kusuda S, et al. (2014) Brief Parenteral Nutrition Accelerates Weight Gain, Head Growth Even in Healthy VLBWs. PLoS ONE 9(2): e88392 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088392 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

