Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor P1446A Induces Apoptosis in a JNK/p38 MAPK-Dependent Manner in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B-Cells
- PMID: 26606677
- PMCID: PMC4659573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143685
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor P1446A Induces Apoptosis in a JNK/p38 MAPK-Dependent Manner in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B-Cells
Abstract
CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitors have shown remarkable activity in CLL, where its efficacy has been linked to inhibition of the transcriptional CDKs (7 and 9) and deregulation of RNA polymerase and short-lived pro-survival proteins such as MCL1. Furthermore, ER (endoplasmic reticulum) stress has been implicated in CDK inhibition in CLL. Here we conducted a pre-clinical study of a novel orally active kinase inhibitor P1446A in CLL B-cells. P1446A inhibited CDKs at nanomolar concentrations and induced rapid apoptosis of CLL cells in vitro, irrespective of chromosomal abnormalities or IGHV mutational status. Apoptosis preceded inactivation of RNA polymerase, and was accompanied by phosphorylation of stress kinases JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) and p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase). Pharmacologic inhibitors of JNK/p38 MAPK conferred protection from P1446A-mediated apoptosis. Treatment with P1446A led to a dramatic induction of NOXA in a JNK-dependent manner, and sensitized CLL cells to ABT-737, a BH3-mimetic. We observed concurrent activation of apoptosis stress-inducing kinase 1 (ASK1) and its interaction with inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) in CLL cells treated with P1446A, providing insights into upstream regulation of JNK in this setting. Consistent with previous reports on limited functionality of ER stress mechanism in CLL cells, treatment with P1446A failed to induce an extensive unfolded protein response. This study provides rationale for additional investigations of P1446A in CLL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
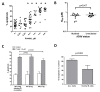

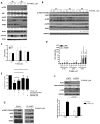

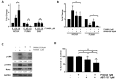
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

