Microfluidic Bioprinting of Heterogeneous 3D Tissue Constructs Using Low-Viscosity Bioink
- PMID: 26606883
- PMCID: PMC4804470
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201503310
Microfluidic Bioprinting of Heterogeneous 3D Tissue Constructs Using Low-Viscosity Bioink
Abstract
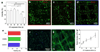
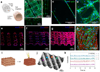
A novel bioink and a dispensing technique for 3D tissue-engineering applications are presented. The technique incorporates a coaxial extrusion needle using a low-viscosity cell-laden bioink to produce highly defined 3D biostructures. The extrusion system is then coupled to a microfluidic device to control the bioink arrangement deposition, demonstrating the versatility of the bioprinting technique. This low-viscosity cell-responsive bioink promotes cell migration and alignment within each fiber organizing the encapsulated cells.
Keywords: 3D tissue engineering; bioinks; bioprinting; microfluidics; vascular tissue engineering.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Atala A, Kasper FK, Mikos AG. Science translational medicine. 2012;4:160rv12. - PubMed
-
- Hardin JO, Ober TJ, Valentine AD, Lewis JA. Advanced materials. 2015;27:3279. - PubMed
-
- Chang CC, Boland ED, Williams SK, Hoying JB. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part B, Applied biomaterials. 2011;98:160. - PMC - PubMed
- Duan B, Hockaday LA, Kang KH, Butcher JT. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A. 2013;101:1255. - PMC - PubMed
- Schuurman W, Khristov V, Pot MW, van Weeren PR, Dhert WJ, Malda J. Biofabrication. 2011;3:021001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

