Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Triazole-Pyrimidine Analogues as SecA Inhibitors
- PMID: 26607404
- PMCID: PMC4778717
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201500447
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Triazole-Pyrimidine Analogues as SecA Inhibitors
Abstract
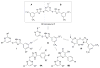
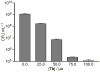
SecA, a key component of the bacterial Sec-dependent secretion pathway, is an attractive target for the development of new antimicrobial agents. Through a combination of virtual screening and experimental exploration of the surrounding chemical space, we identified a hit bistriazole SecA inhibitor, SCA-21, and studied a series of analogues by systematic dissections of the core scaffold. Evaluation of these analogues allowed us to establish an initial structure-activity relationship in SecA inhibition. The best compounds in this group are potent inhibitors of SecA-dependent protein-conducting channel activity and protein translocation activity at low- to sub-micromolar concentrations. They also have minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values against various strains of bacteria that correlate well with the SecA and protein translocation inhibition data. These compounds are effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains with various levels of efflux pump activity, indicating the capacity of SecA inhibitors to null the effect of multidrug resistance. Results from studies of drug-affinity-responsive target stability and protein pull-down assays are consistent with SecA as a target for these compounds.
Keywords: SecA inhibitors; antimicrobials; protein secretion; pyrimidines; triazoles.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




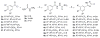


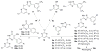
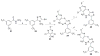
References
-
- Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, Scheld M, Spellberg B, Bartlett J. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:1–12. - PubMed
- CDC. 2013
- Fernández L, Gooderham WJ, Bains M, McPhee JB, Wiegand I, Hancock REW. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3372–3382. - PMC - PubMed
- Kaatz GW, McAleese F, Seo SM. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:1857–1864. - PMC - PubMed
- Chopra I, Schofield C, Everett M, O’Neill A, Miller K, Wilcox M, Frère JM, Dawson M, Czaplewski L, Urleb U, Courvalin C. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Gold VAM, Whitehouse S, Robson A, Collinson I. Biochem J. 2013;449:695–705. - PMC - PubMed
- Or E, Boyd D, Gon S, Beckwith J, Rapoport T. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:9097–9105. - PubMed
- Economou A. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2001;5:141–153. - PubMed
- Abe A. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2009;83:94–100. - PubMed
- Lee VT, Schneewind O. Genes Dev. 2001;15:1725–1752. - PubMed
- Scott JR, Barnett TC. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2006;60:397–423. - PubMed
-
- Segers K, Klaassen H, Economou A, Chaltin P, Anné J. Anal Biochem. 2011;413:90–96. - PubMed
- Hsieh YH, Huang Y, Jin J, Yu L, Yang H, Jiang C, Wang B, Tai PC. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;454:308–312. - PMC - PubMed
- Jin J, Cui J, Chaudhary AS, Hsieh Y, Damera K, Zhang H, Yang H, Wang B, Tai PC. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.1009.1027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Chaudhary AS, Chen W, Jin J, Tai PC, Wang B. Future Med Chem. 2015;7:989–1007. - PMC - PubMed
- Huang YJ, Wang H, Gao FB, Li M, Yang H, Wang B, Tai PC. ChemMedChem. 2012;7:571–577. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schmidt MG, Rollo EE, Grodberg J, Oliver DB. J Bacteriol. 1988;170:3404–3414. - PMC - PubMed
- Magiorakosa AP, Srinivasanb A, Careyb RB, Carmelic Y, Falagasd ME, Giskef CG, Harbarthg S, Hindlerh JF, Kahlmeteri G, Olsson–Liljequistj B, Patersonk DL, Ricel LB, Stellingm J, Struelensa MJ, Vatopoulosn A, Weberb JT, Monneta DL. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;8:268–281. - PubMed
- Siboo IR, Chaffin DO, Rubens CE, Sullam PM. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:6188–6196. - PMC - PubMed
- Rigel NWBM. Mol Microbiol. 2008;69:291–302. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

