Promoter-based identification of novel non-coding RNAs reveals the presence of dicistronic snoRNA-miRNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 26607788
- PMCID: PMC4660826
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2221-x
Promoter-based identification of novel non-coding RNAs reveals the presence of dicistronic snoRNA-miRNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
Background: In the past few decades, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have emerged as important regulators of gene expression in eukaryotes. Most studies of ncRNAs in plants have focused on the identification of silencing microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Another important family of ncRNAs that has been well characterized in plants is the small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and the related small Cajal body-specific RNAs (scaRNAs). Both target chemical modifications of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). In plants, the snoRNA genes are organized in clusters, transcribed by RNA Pol II from a common promoter and subsequently processed into mature molecules. The promoter regions of snoRNA polycistronic genes in plants are highly enriched in two conserved cis-regulatory elements (CREs), Telo-box and Site II, which coordinate the expression of snoRNAs and ribosomal protein coding genes throughout the cell cycle.
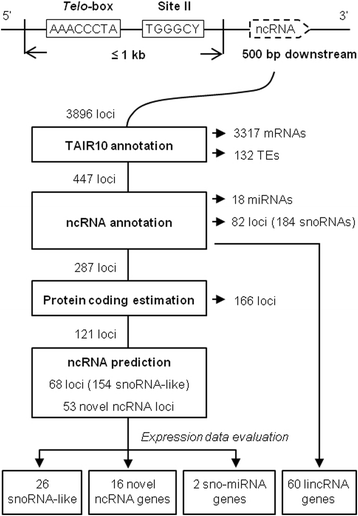
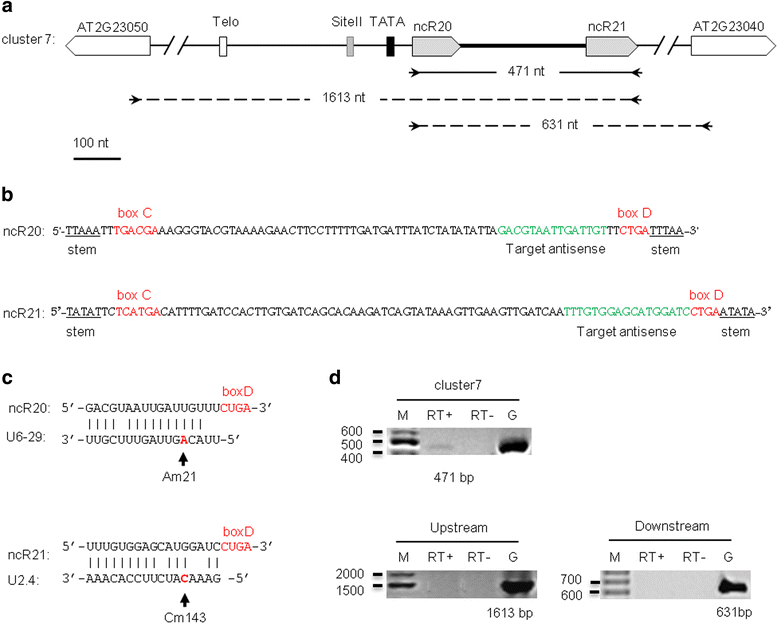
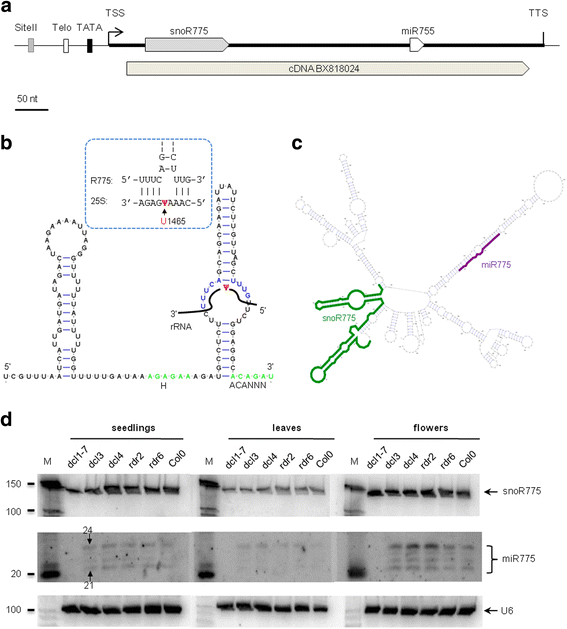
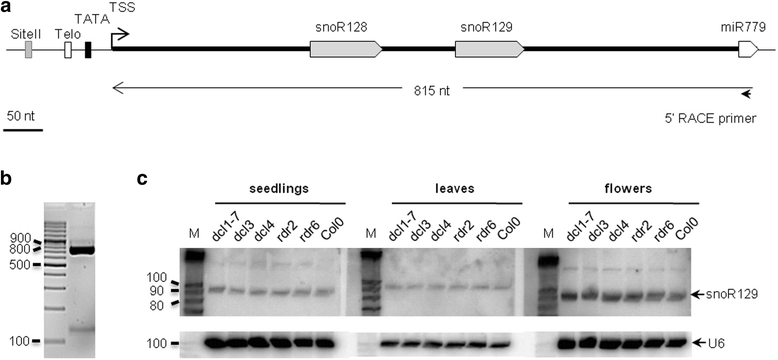
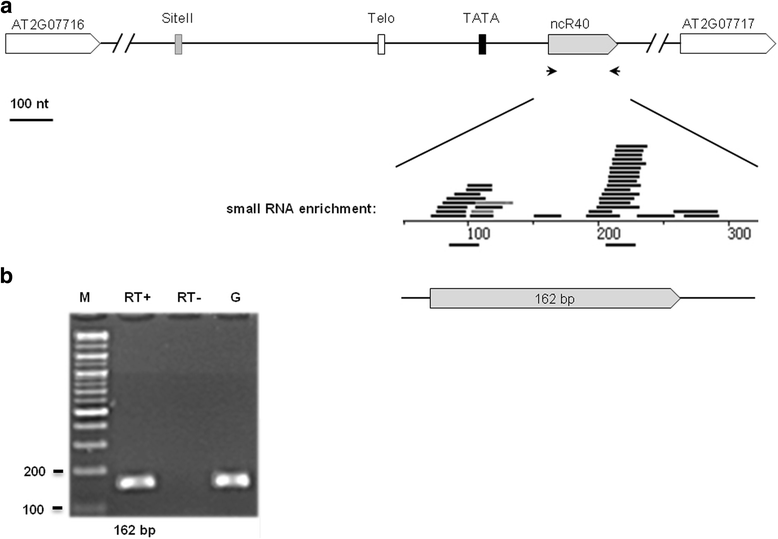
Results: In order to identify novel ncRNA genes, we have used the snoRNA Telo-box/Site II motifs combination as a functional promoter indicator to screen the Arabidopsis genome. The predictions generated by this process were tested by detailed exploration of available RNA-Seq and expression data sets and experimental validation. As a result, we have identified several snoRNAs, scaRNAs and 'orphan' snoRNAs. We also show evidence for 16 novel ncRNAs that lack similarity to any reported RNA family. Finally, we have identified two dicistronic genes encoding precursors that are processed to mature snoRNA and miRNA molecules. We discuss the evolutionary consequences of this result in the context of a tight link between snoRNAs and miRNAs in eukaryotes.
Conclusions: We present an alternative computational approach for non-coding RNA detection. Instead of depending on sequence or structure similarity in the whole genome screenings, we have explored the properties of promoter regions of well-characterized ncRNAs. Interestingly, besides expected ncRNAs predictions we were also able to recover single precursor arrangement for snoRNA-miRNA. Accompanied by analyses performed on rice sequences, we conclude that such arrangement might have interesting functional and evolutionary consequences and discuss this result in the context of a tight link between snoRNAs and miRNAs in eukaryotes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human miRNA precursors with box H/ACA snoRNA features.PLoS Comput Biol. 2009 Sep;5(9):e1000507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000507. Epub 2009 Sep 18. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 19763159 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 66 box C/D snoRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana: extensive gene duplications generated multiple isoforms predicting new ribosomal RNA 2'-O-methylation sites.J Mol Biol. 2001 Aug 3;311(1):57-73. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4851. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11469857
-
Plant dicistronic tRNA-snoRNA genes: a new mode of expression of the small nucleolar RNAs processed by RNase Z.EMBO J. 2003 Feb 3;22(3):621-32. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg040. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12554662 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2007 Nov;72(11):1161-78. doi: 10.1134/s0006297907110016. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2007. PMID: 18205598 Review.
-
The many faces of small nucleolar RNAs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jun;1839(6):438-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24735946 Review.
Cited by
-
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) snoRNAome.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2025 Mar 5;7(1):lqaf013. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqaf013. eCollection 2025 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40046902 Free PMC article.
-
Linking discoveries, mechanisms, and technologies to develop a clearer perspective on plant long noncoding RNAs.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1762-1786. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad027. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36738093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNORD1C maintains stemness and 5-FU resistance by activation of Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Apr 14;8(1):200. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00996-5. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35422067 Free PMC article.
-
A Conserved Long Intergenic Non-coding RNA Containing snoRNA Sequences, lncCOBRA1, Affects Arabidopsis Germination and Development.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 25;13:906603. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.906603. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35693169 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping rRNA 2'-O-methylations and identification of C/D snoRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana plants.RNA Biol. 2021 Nov;18(11):1760-1777. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1869892. Epub 2021 Feb 17. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33596769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattick JS, Rinn JL. Discovery and annotation of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Publ Gr. 2015;22:5–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

