Effects of albendazole combined with TSII-A (a Chinese herb compound) on optic neuritis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in BALB/c mice
- PMID: 26608105
- PMCID: PMC4660773
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-015-1214-6
Effects of albendazole combined with TSII-A (a Chinese herb compound) on optic neuritis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in BALB/c mice
Abstract
Background: Angiostrongylus cantonensis (A. cantonensis) infection can lead to optic neuritis, retinal inflammation, damage to ganglion cells, demyelination of optic nerve and visual impairment. Combined therapy of albendazole and dexamethasone is a common treatment for the disease in the clinic, but it plays no role in vision recovery. Therefore, it has been necessary to explore alternative therapies to treat this disease. Previous studies reported the neuro-productive effects of two constituents of Danshen (a Chinese herb)-tanshinone II-A (TSII-A) and cryptotanshinone (CPT), and this study aims to evaluate the impacts of TSII-A or CPT combined with albendazole on optic neuritis caused by A. cantonensis infection in a murine model.
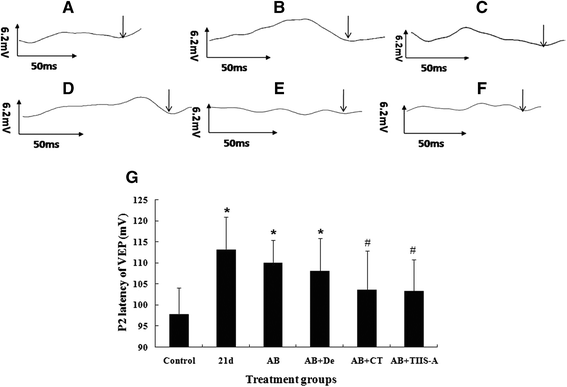
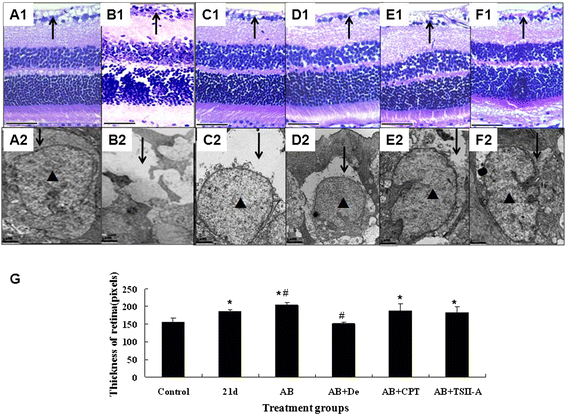
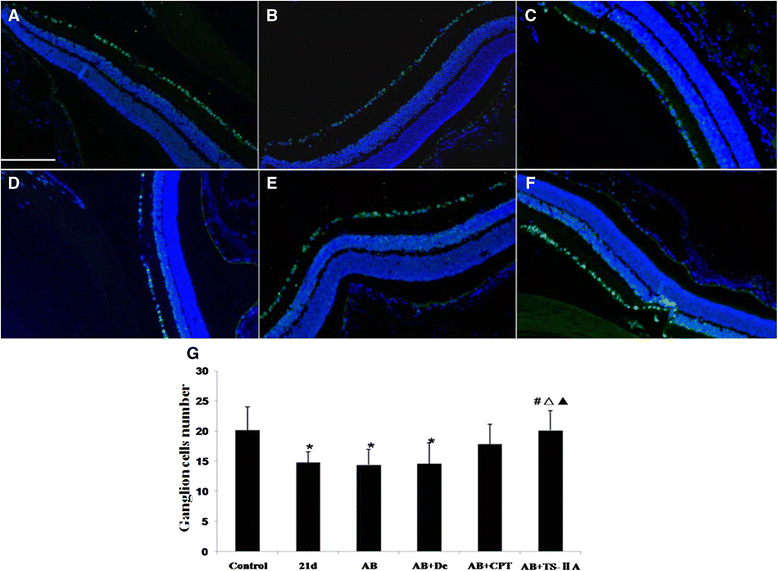
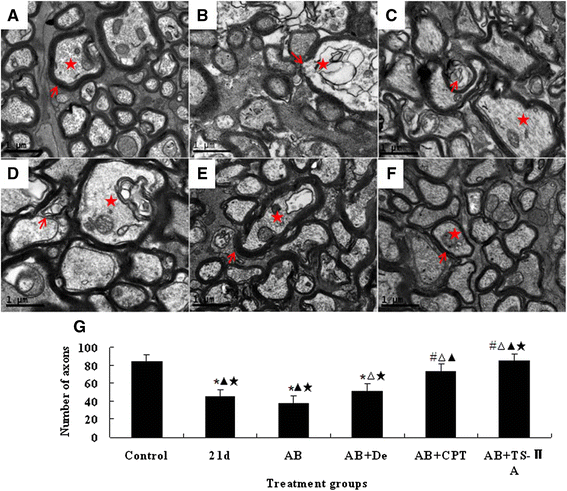
Methods: To assess the effects of TSII-A or CPT combined with albendazole on optic neuritis due to the infection, mice were divided into six groups, including the normal control group, infection group and four treatment groups (albendazole group, albendazole combined with dexamethasone group, albendazole combined with CPT group and albendazole combined with TSII-A group). The infection group and treatment groups were infected with A. cantonensis and the treatment groups received interventions from 14 dpi (days post infection), respectively. At 21 dpi, the visual acuity of mice in each group was examined by visual evoked potential (VEP). The pathologic alteration of the retina and optic nerve were observed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and transmission electronic microscopy (TEM).
Results: Infection of A. cantonensis caused prolonged VEP latency, obvious inflammatory cell infiltration in the retina, damaged retinal ganglions and retinal swelling, followed by optic nerve fibre demyelination and a decreasing number of axons at 21 dpi. In treatment groups, albendazole could not alleviate the above symptoms; albendazole combined with dexamethasone lessened the inflammation of the retina, but was futile for the other changes; however, albendazole combined with CPT and albendazole combined with TSII-A showed obvious effects on the recovery of prolonged VEP latency, destruction and reduction of ganglion cells, optic nerve demyelination and axon loss. Compared with albendazole-CPT compound, albendazole combined with TSII-A was more effective.
Conclusions: The current study demonstrates that albendazole combined with TSII-A plays a more effective role in treating optic neuritis caused by A. cantonensis in mice than with dexamethasone, as applied in conventional treatment, indicating that albendazole combined with TSII-A might be an alternate therapy for this parasitic disease in the clinic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Animal model of human disease with optic neuritis: neuropapillitis in a rat model infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis.Parasitol Res. 2014 Nov;113(11):4005-13. doi: 10.1007/s00436-014-4067-6. Epub 2014 Aug 31. Parasitol Res. 2014. PMID: 25172599
-
The pathogenesis of optic neuritis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in BALB/c mice.Parasit Vectors. 2014 Jul 22;7:339. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-339. Parasit Vectors. 2014. PMID: 25052055 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin alleviates eosinophilic meningitis through reduction of eosinophil count following albendazole treatment against Angiostrongylus cantonensis in mice.Parasitology. 2012 Mar;139(3):358-65. doi: 10.1017/S0031182011001922. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Parasitology. 2012. PMID: 22053741
-
Comprehensive review of ocular angiostrongyliasis with special reference to optic neuritis.Korean J Parasitol. 2013 Dec;51(6):613-9. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2013.51.6.613. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Korean J Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 24516263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Past, present, and future in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Dec;105(12):809-27. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11802455 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde enhance survival of mouse astrocytes treated with Angiostrongylus cantonensis young adults excretory/secretory products.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6 Suppl 2):S258-S266. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.11.008. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 35300947 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Albendazole and Other Benzimidazole Anthelmintics for Rat Lungworm Disease (Neuroangiostrongyliasis): A Systematic Analysis of Clinical Reports and Animal Studies.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Apr 9;74(7):1293-1302. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab730. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34448480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico prediction of flavan-3-ol as a bioactive compound of Calophyllum macrophyllum as a potential drug against angiostrongylus eosinophilic meningitis.Vet World. 2022 May;15(5):1305-1313. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.1305-1313. Epub 2022 May 25. Vet World. 2022. PMID: 35765470 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Interleukin 17 Can Ameliorate the Demyelination Caused by A. cantonensis via iNOS Inhibition.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:3513651. doi: 10.1155/2017/3513651. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29403160 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-letting therapy combined with Master Tung's Five-tiger Point Scraping (Gua Sha) for patients with hematological malignancy and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuritis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Aug 15;15(8):5304-5313. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37692923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ketsuwan PPA. Second case of ocular angiostrongyliasis in Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966;15(1):50–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

