Identification and characterization of transcriptional control region of the human beta 1,4-mannosyltransferase gene
- PMID: 26608959
- PMCID: PMC5461232
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-015-9929-y
Identification and characterization of transcriptional control region of the human beta 1,4-mannosyltransferase gene
Abstract
All asparagine-linked glycans (N-glycans) on the eukaryotic glycoproteins are primarily derived from dolichol-linked oligosaccharides (DLO), synthesized on the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane. We have previously reported cloning and identification of the human gene, HMT-1, which encodes chitobiosyldiphosphodolichol beta-mannosyltransferase (β1,4-MT) involved in the early assembly of DLO. Considering that N-glycosylation is one of the most ubiquitous post-translational modifications for many eukaryotic proteins, the HMT-1 could be postulated as one of the housekeeping genes, but its transcriptional regulation remains to be investigated. Here we screened a 1 kb region upstream from HMT-1 open reading frame (ORF) for transcriptionally regulatory sequences by using chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) assay, and found that the region from -33 to -1 positions might act in HMT-1 transcription at basal level and that the region from -200 to -42 should regulate its transcription either positively or negatively. In addition, results with CAT assays suggested the possibility that two GATA-1 motifs and an Sp1 motif within a 200 bp region upstream from HMT-1 ORF might significantly upregulate HMT-1 transcription. On the contrary, the observations obtained from site-directed mutational analyses revealed that an NF-1/AP-2 overlapping motif located at -148 to -134 positions should serve as a strong silencer. The control of the HMT-1 transcription by these motifs resided within the 200 bp region could partially explain the variation of expression level among various human tissues, suggesting availability and importance of this region for regulatory role in HMT-1 expression.
Keywords: Dolichol-linked oligosaccharide; Gene expression; Mannosyltransferase; N-glycosylation; Transcription.
Figures
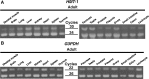
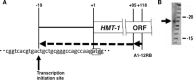




References
-
- Adamowicz M, Chmielinska E, Kaluzny L, Bittner G, Sarnowska-Wroczynska I, Timal S, Morava E, Lehle L, Wevers RA, Lefeber DJ, Sykut-Cegielska J. Clinical and biochemical characterization of the second CDGIJ (DPAGT1-CDG) patient. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011;34:S181. doi: 10.1007/s10545-010-9249-5. - DOI
-
- Albright CF, Robbins PW. The sequence and transcript heterogeneity of the yeast gene ALG1, an essential mannosyltransferase involved in N-glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7042–7049. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

