Multibiomarker disease activity score and C-reactive protein in a cross-sectional observational study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with and without concomitant fibromyalgia
- PMID: 26608972
- PMCID: PMC4795537
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev388
Multibiomarker disease activity score and C-reactive protein in a cross-sectional observational study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with and without concomitant fibromyalgia
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the association between a multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) score, CRP and clinical disease activity measures among RA patients with and without concomitant FM.
Methods: In an observational cohort of patients with established RA, we performed a cross-sectional analysis comparing MBDA scores with CRP by rank correlation and cross-classification. MBDA scores, CRP and clinical measures of disease activity were compared between patients with RA alone and RA with concomitant FM (RA and FM) by univariate and multivariate analyses.
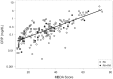
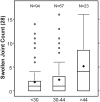
Results: CRP was ⩽1.0 mg/dl for 184 of 198 patients (93%). MBDA scores correlated with CRP (r = 0.755, P < 0.001), but were often discordant, being moderate or high for 19%, 55% and 87% of patients with CRP ⩽0.1, 0.1 to ⩽0.3, or 0.3 to ⩽1.0 mg/dl, respectively. Among patients with CRP ⩽1.0 mg/dl, swollen joint count (SJC) increased linearly across levels of MBDA score, both with (P = 0.021) and without (P = 0.004) adjustment for CRP, whereas CRP was not associated with SJC. The 28-joint-DAS-CRP, other composite measures, and their non-joint-count component measures were significantly greater for patients with RA and FM (n = 25) versus RA alone (n = 173) (all P ⩽ 0.005). MBDA scores and CRP were similar between groups.
Conclusion: MBDA scores frequently indicated RA disease activity when CRP did not. Neither one was significantly greater among patients with RA and FM versus RA alone. Thus, MBDA score may be a useful objective measure for identifying RA patients with active inflammation when CRP is low (⩽1.0 mg/dl), including RA patients with concomitant FM.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; RAPID3; biomarkers; disease activity; fibromyalgia; multibiomarker; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Brown AK, Conaghan PG, Karim Z. et al. An explanation for the apparent dissociation between clinical remission and continued structural deterioration in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:2958–67. - PubMed
-
- Crowson CS, Rahman MU, Matteson EL. Which measure of inflammation to use? A comparison of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein measurements from randomized clinical trials of golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2009;36:1606–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

